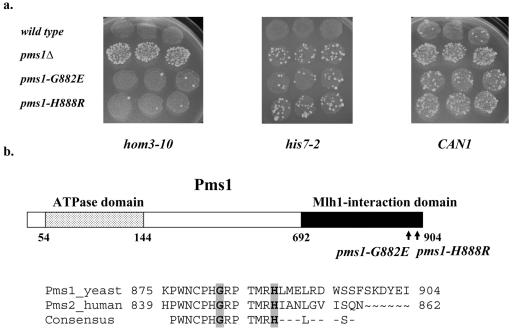
FIG. 2.
(a) Papillation phenotypes of the wild-type, pms1Δ, pms1-G882E, and pms1-H888R strains. The relative mutator effects at hom3-10, his7-2, and CAN1 alleles in wild-type, pms1Δ, pms1-G882E, and pms1-H888R strains were detected initially by monitoring reversion at hom3-10 and his7-2 and the forward mutation of CAN1 alleles individually by replica plating patches of cells onto appropriate selective media. (b) Pms1 domains and location of altered Pms1 residues. The ATPase domain (residues 54 to 144) and the Mlh1-interacting domain (residues 692 to 904) are indicated by dotted and black boxes, respectively. Also shown are the residues corresponding to the COOH termini of yeast and human homologs. The mutated residues, G882 and H888, are shaded gray. The 13-amino-acid domain, identical between yeast and human homologs, is depicted below the alignment of yeast and human homolog sequences. Numbers correspond to the amino acid position in the protein.