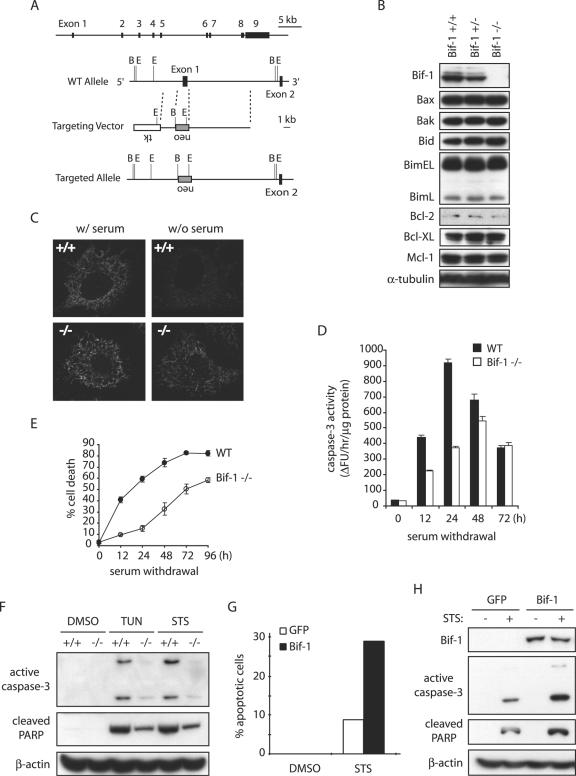
FIG. 4.
Knockout of Bif-1 in MEFs delays mitochondrial apoptosis. (A) Genomic organization of the mouse bif-1 gene, targeting construct, and targeted locus. The restriction enzyme sites shown are B (BamHI) and E (EcoRI). WT, wild type. (B) Immunoblot analysis of whole-cell lysates from Bif-1+/+, Bif-1+/−, and Bif-1−/− embryonic day 12.5 mouse embryos. (C) Bif-1+/+ and Bif-1−/− MEFs were cultured in the presence or absence of serum for 6 h and applied to immunostaining with anti-cytochrome c antibody. (D and E) Bif-1−/− and WT MEFs were cultured with or without serum for various times before caspase 3 activity analysis (D) and trypan blue dye exclusion assay (E). The error bars indicate standard deviations. (F) Bif-1−/− and Bif-1+/+ MEFs were treated with 1 μg/ml TUN for 24 h, 1 μM STS for 12 h, or DMSO as a control. Cell lysates were prepared in CHAPS lysis buffer and analyzed by SDS-PAGE/immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies. (G and H) Bif-1−/− MEFs were transfected with 10 μg of pIRES2-EGFP vector or pBif-1-IRES2-EGFP plasmid DNA for 40 h using the Nucleofector technology (Amaxa) and subjected to treatment with DMSO or 1 μM STS for 12 h. The percentage of apoptotic GFP-positive cells was determined by DAPI staining assay (G), and cell lysates were prepared and analyzed by SDS-PAGE/immunoblotting (H).