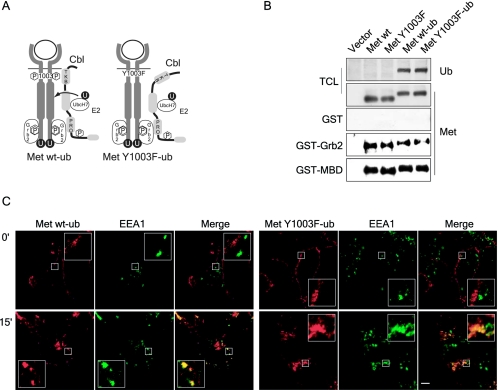
FIG. 7.
Fusion of monoubiquitin to the carboxy terminus of the Met receptor does not alter its maturation to the cell surface, recruitment of signaling proteins and its HGF-induced internalization. (A) Schematic representation of ubiquitinated wild-type and Y1003 Met chimeric receptors. Met receptor chimeras were generated with a single ubiquitin moiety fused to the carboxy-terminal end of the full-length wild-type and Y1003F Met receptors. The seven lysine residues within the ubiquitin moiety were replaced with arginine residues to prevent polyubiquitination and the carboxy-terminal glycine residue was replaced with a valine residue to prevent conjugation to free amino groups. (B) The chimeric receptors are properly expressed and tyrosine phosphorylated. HEK 293 cells were transiently transfected with the indicated CSF-Met constructs. In the top two panels, lysates were blotted with Met (antibody 144) and ubiquitin antibodies. In the bottom three panels, lysates were incubated with GST alone, GST-Grb2, or GST-MBD (Met binding domain of Gab1). In vitro binding assays and total cell lysates (TCL) were immunoblotted for Met. (C) T47D cells were plated on coverslips and 16 h later stimulated with 1.5 nM HGF at 37°C for 15 min. Coverslips were fixed in 3% PFA and stained with Met AF276 (red) and EEA1 (green) antibodies. Confocal images were taken with a 100× objective and 2× zoom. Yellow staining represents colocalization between Met and EEA1. The bar represents 5 μm.