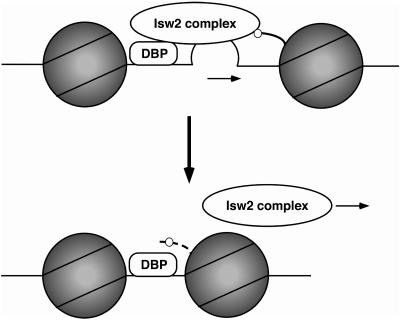
FIG. 7.
A model for Isw2-dependent chromatin remodeling in vivo. (Top) Isw2 is targeted to specific loci via interactions with sequence-specific DNA binding proteins (DBP), linker DNA (bulge), and the basic patch (small circle) of the histone H4 tail (thick curved line). These interactions allow Isw2 to generate the necessary force to push DNA into nucleosomes (arrow). (Bottom) After nucleosome sliding, Isw2 is released from its targets as shown by an arrow. This may be due to the lack of sufficiently long linker DNA, reduced availability of histone H4 tail (dashed line), or a combination of both after remodeling.