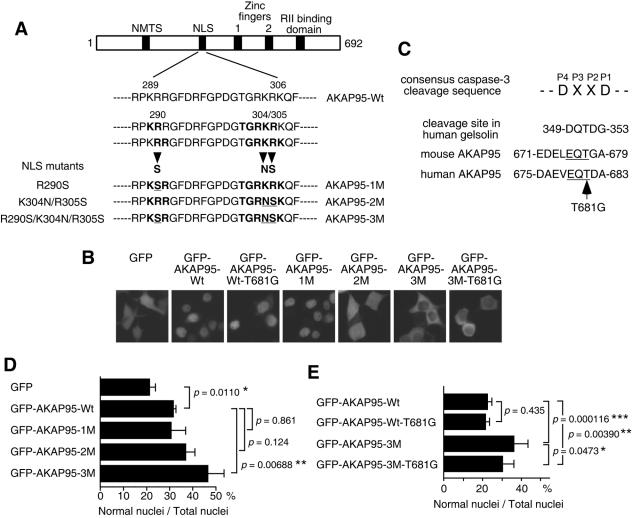
FIG. 5.
Function of AKAP95 in nuclear morphological changes of apoptotic cells. (A) Diagram showing the NLS mutations of AKAP95. Mutated amino acid residues are underlined. NMTS, nuclear matrix targeting site; RII, type II PKA regulatory subunit. (B) Localization of GFP-AKAP95 fusion proteins with or without mutations. 293T cells were transiently transfected with GFP or GFP-AKAP95 expression plasmids as indicated. After 18 h, cells were observed by fluorescence microscopy. (C) Amino acid sequences of active caspase 3 binding region in AKAP95. Conserved EQT sequence between human and mouse AKAP95 is underlined. (D and E) Overexpression of AKAP95 with NLS mutations inhibits nuclear morphological changes. HepG2 cells were transfected with GFP-AKAP95 expression plasmids as indicated. After 24 h, cells were treated with an agonistic anti-Fas antibody in the presence of actinomycin D for 12 h (D) or 15 h (E) and collected and fixed with 3.7% formaldehyde for 10 min. After staining with Hoechst 33342, the percentage of the cells showing normal nuclei to the total transfected cells was measured. At least 100 GFP-positive cells were counted for each measurement in all experiments. The data (mean ± the standard deviation) were obtained from at least three independent experiments. Significant test results (P values) are shown. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001.