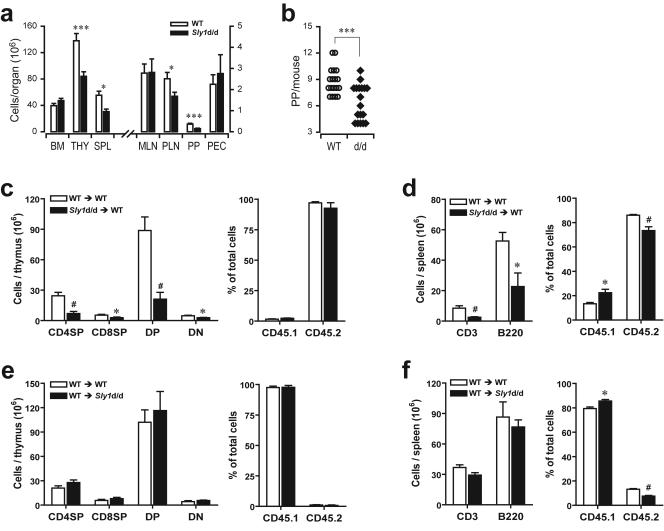
FIG. 2.
Influence of the Sly1d/d mutation on lymphoid organogenesis. (a) Total cell numbers were determined from bone marrow (BM), thymus (THY), spleen (SPL), mesenteric (MLN) and peripheral (PLN) lymph nodes, Peyer's patches (PP), and in peritoneal lavage (PEC) of wild-type littermates (white bars) and Sly1 mutant mice (solid bars) with 18 mice analyzed in each group. (b) Numbers of macroscopically visible Peyer's patches were counted. Each symbol represents an individual mouse (WT, wild-type littermate controls; d/d, Sly1 mutant mice). (c and e) Chimeric mice were generated by adoptive transfer of bone marrow cells from wild-type or Sly1d/d mice (both CD45.2+) into lethally irradiated CD45.1+ wild-type recipients or (d and f) by injection of CD45.1+ wild-type bone marrow cells into CD45.2+ wild-type and Sly1d/d recipients. Recipient mice were analyzed 4 weeks after adoptive transfer for CD4/CD8-defined thymic subsets (c and e) and the presence of CD3+ and B220+ cells in spleen (d and f). Results of adoptive transfer experiments are derived from 4 or 5 mice per group. *, P < 0.05; #, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001 (Student's t test). DP, double-positive; DN, double-negative.