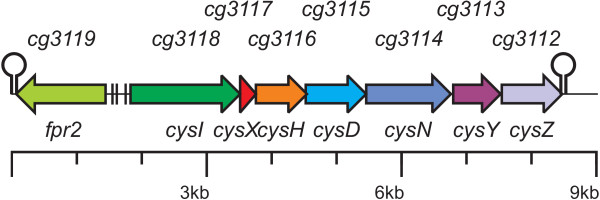
Figure 1.
The fpr2cysIXHDNYZ gene cluster in the C. glutamicum genome. Coloured arrows indicate genes that are part of the cluster most probably involved in assimilatory sulphate reduction. Hairpins mark potential rho-independent transcription termination signals predicted by the TransTerm software. Black bars denote binding sites for the transcriptional repressor McbR [15].