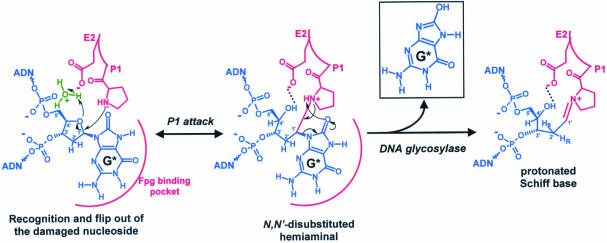
Figure 7.
The ring-opened form of the damaged base deoxyribose is the sugar active form for Fpg catalysis. After the recognition and the flip out of the damaged nucleoside inner the Fpg substrate binding pocket, the P1 nucleophile attacks the anomeric C1′ carbon to form a transient aminal intermediate in which E2 acts as general acid catalyst. Thus, expulsion of the damaged base leaving group occurs in the subsequent step of forming the protonated Schiff base intermediate. The catalytic E2 could now stabilize the cationic Schiff base intermediate through a favourable electrostatic interaction, providing the thermodynamic driving force for expulsion of the damaged base. G* indicates 8-oxoG. A similar molecular mechanism can be drawn for the Fapy residue as substrate.