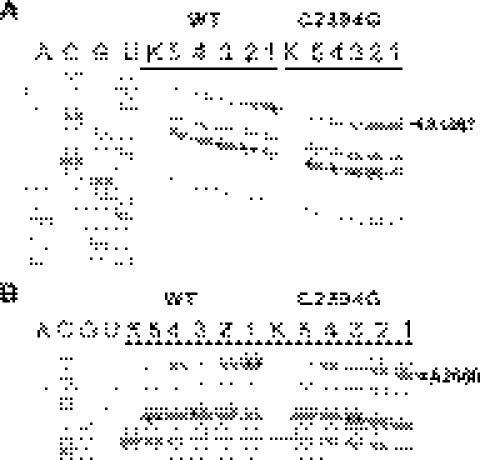
Figure 4.
Interaction of ribosomes carrying the C2394G mutation with EF-G, monitored by footprinting. (A) DMS footprints of EF-G on the GAC of the wild-type (WT) and mutant (C2394G) ribosomes. (A, C, G, U)—correspond to sequencing lanes; (K)—to the unmodified rRNA. Other lanes of the gel are marked according to the ribosomal complex, modified with DMS. (1) empty ribosomes; (2) ribosomes, MFK-mRNA, fMet-, Phe-tRNAPhe*EF-Tu*GTP, EF-G*GMPPNP; (3) ribosomes, MFK-mRNA, fMet-, Phe-tRNAPhe*EF-Tu*GTP, EF-G*GTP, fusidic acid; (4) ribosomes, EF-G*GMPPNP; (5) ribosomes, EF-G*GTP, fusidic acid. The primer extension stop corresponding to the nucleotide A1067 protected from DMS modification by EF-G is marked. (B) DMS footprints of EF-G on the Sarcin–Ricin loop of the wild-type and mutant ribosomes. Lanes are marked as in (A). The primer extension stop corresponding to the nucleotide A2660 protected from DMS modification by EF-G is marked.