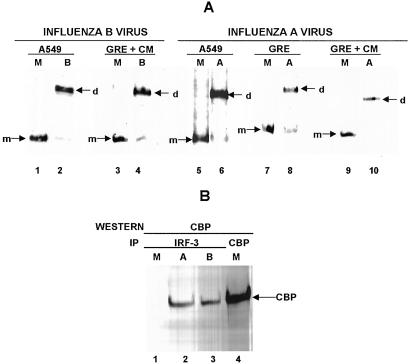
Figure 3.
Activation of IRF-3 by either influenza A virus or influenza B virus is not mediated by IFN-α/β and does not require the synthesis of virus-encoded proteins. (A) IRF-3 dimerization assay. A549 cells were either mock-infected (M, lanes 1 and 5), or infected for 4 h with either influenza B virus (B, lane 2) or influenza A virus (A, lane 6). GRE cells were either mock-infected (M, lane 7), or infected for 4 h with influenza A virus (A, lane 8). GRE cells in the presence of CM were either mock-infected (M, lanes 3 and 9), or infected for 4 h with either influenza B virus (B, lane 4) or influenza A virus (A, lane 10). An aliquot of the cell extracts was treated with deoxycholate and subjected to electrophoresis on a 7.5% native gel. The monomer (m) and dimer (d) forms of IRF-3 were identified by immunoblotting with the SL-12 monoclonal antibody. (B) Association of CBP with IRF-3 after influenza A or B virus infection. A549 cells were either mock-infected (M, lane 1), or infected for 4 h with either influenza A virus (lane 2) or influenza B virus (B, lane 3). Cell extracts were immunoprecipitated with the SL-12 antibody (anti-IRF-3), and immunoprecipitates were analyzed by Western blots with CBP antibody. Lane 4, cell extract from mock-infected cells was immunoprecipitated with CBP antibody to provide a marker lane for CBP.