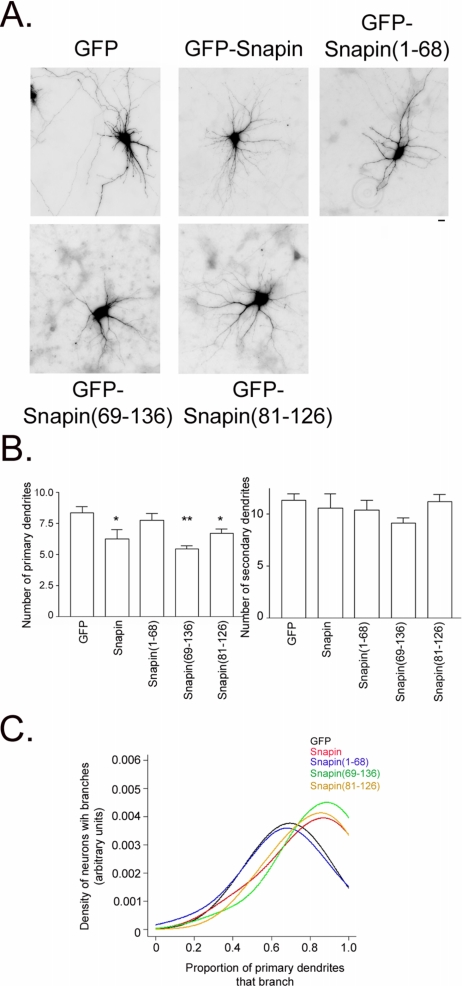
Figure 6.
Snapin affects dendrite patterning. (A) Representative neurons transfected with cDNA encoding GFP, GFP-snapin, GFP-snapin(1-68), GFP-snapin(69-136), or GFP-snapin(81-126). Bar, 10 μm. (B) Average number of primary and secondary dendrites in neurons that overexpress GFP (n = 74), GFP-snapin (n = 12), GFP-snapin(1-68) (n = 22), GFP-snapin(69-136) (n = 36), or GFP-snapin(81-126) (n = 29). Snapin proteins that bind to cypin [snapin, snapin(69-136), snapin(81-126)] decrease primary dendrite number but do not affect secondary dendrite number. *p < 0.05 and **p < 0.01 by ANOVA followed by Dunnett's multiple comparison test compared with GFP control. (C) Snapin, snapin(69-136), and snapin(81-126) but not snapin(1-68) increase probability of dendrite branching. Data from B were plotted as a distribution of primary dendrites that branch. The graph clearly indicates that the branching probability is higher for snapin (red line), snapin(69-136) (green line), and GFP-snapin(81-126) (yellow line) compared with snapin(1-68) (blue line) and GFP (black line). GFP and GFP-snapin(1-68) do not differ from each other (p > 0.05) nor do GFP-snapin, GFP-snapin(69-136), and GFP-snapin (81-26) differ from each other (p > 0.05), but the two groups differ from each other (p < 0.001).