Figure 4.
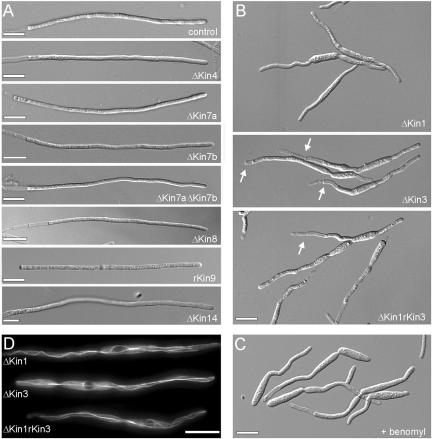
Morphology phenotype of kinesin null mutants. (A) Most kinesin null mutants neither have defects in the yeast-like stage (our unpublished data) nor show impaired hyphal growth. Note that most mutants are in the ABB33 background (see Materials and Methods), whereas Δkin14 hyphae were obtained from crossing compatible mutant strains on charcoal plates. All bars, 10 μm. (B) Δkin1 and Δkin3 mutant hyphae often grow in a bipolar manner and are unable to form long filaments. No additional defects were seen in Δkin1rkin3 double mutants. Note that, for unknown reason, the double mutants again formed vacuolated hyphal parts. Bar, 10 μm. (C) Treatment of AB33 hyphae with 10 μM benomyl for 12 h resulted in short hyphae that showed phenotypic similarities to Δkin1 and Δkin3 mutant hyphae. Bar, 10 μm. (D) GFP-labeled MTs were normal in Δkin1 and Δkin3 mutants (see Steinberg et al., 2001 for MT organization in wild-type cells), which demonstrates that the morphological phenotype of the kinesin mutants is not due to a global defect in MT organization. Bar, 10 μm.