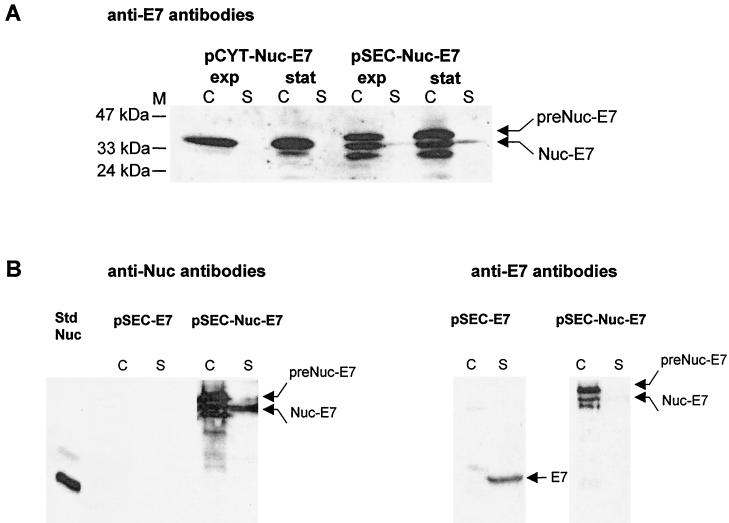
FIG. 3.
(A) Production of Nuc-E7 fusion is stable in L. lactis. Nuc-E7 production was analyzed by Western blot analysis using anti-E7 antibodies on exponential- and stationary-phase cultures of L. lactis strains containing pCYT-Nuc-E7 (encoding Nuc-E7) or pSEC-Nuc-E7 (encoding preNuc-E7). Arrows indicate positions of Nuc-E7 mature and precursor forms. Other bands in the supernatant fraction of L. lactis (pSEC-Nuc-E7) probably correspond to putative products resulting from secondary proteolytic cleavage of Nuc-E7. (B) Estimation of Nuc-E7 (pSEC-Nuc-E7) and native E7 (pSEC-E7) yields in L. lactis. Production yields were estimated for the secreted forms of both Nuc-E7 (pSEC-Nuc-E7) and native E7 (pSEC-E7). The left panel shows quantification of Nuc-E7 production by Western blot analysis using anti-Nuc antibodies. Nuc-E7 signal was compared to the signal of known amounts of commercial Nuc by quantitative scanning of blots after immunodetection (ImageQuant) (19). Total Nuc-E7 concentration is estimated to be around 15 μg/ml, of which about 3 to 5 μg/ml is in the supernatant. The right panel shows the analysis, after dehybridization, of the same membrane using anti-E7 antibodies. Signal intensities of native E7 forms were compared to those of Nuc-E7 forms in the panel at left. Total native E7 concentration is estimated to be about three times less than that of Nuc-E7. Abbreviations: C, cell lysates; S, supernatant fraction (note that culture supernatant samples were concentrated about fivefold prior to loading); M, positions and sizes of molecular weight markers; exp, exponential phase; stat, stationary phase; Std Nuc, NucA standard (50 μg/ml for std Nuc, i.e., 1 μg loaded on the gel; note that the faint higher band corresponds to NucB form enzyme).