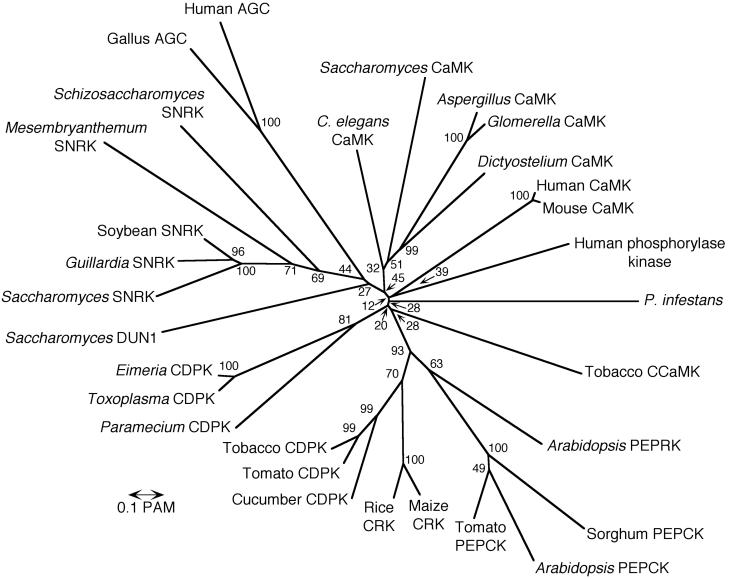
FIG. 4.
Neighbor-joining tree based on kinase domains. A consensus tree was developed based on the amino acid sequence of the 12 kinase domain regions of various serine/threonine protein kinases as described in Materials and Methods. Numbers at nodes indicate the percentages of their occurrence in 500 bootstrap replicates, and the scale represents 0.1 PAM units. The types of kinases examined and their GenBank accession numbers are as follows: CaMKs were from A. nidulans (AAD38850), C. elegans (BAA82674), Dictyostelium discoideum (A40811), Glomerella cingulata (AAC62515), human (NP001212), mouse (AAC48715), and S. cerevisiae (CAA40928). CDPKs (with calmodulin-like domain) were from cucumber (AAB49984), Eimeria tenella (CAA96439), P. tetraurelia (AAC13356), tobacco (AAC25423), tomato (AAK52801), and T. gondii (AF043629). A Ca2+- and/or Ca2+- and calmodulin-regulated kinase (CCaMK) from tobacco (with visinin-like domain) (AAD28791) was also tested. Plant calcium-independent protein kinases (CRKs) were from rice (AAK54157) and maize (BAA22410). PEPCKs were from Arabidopsis (AAK84668), sorghum (AAK81871), and tomato (AAF19403). A PEPCK-related kinase (PEPRK) from Arabidopsis (T45842) was also tested. SNF1-like kinases (SNRKs) were from the algae Guillardia theta (AF165818), Mesembryanthemum crystallinum (Z26846), S. cerevisiae (M13971), Schizosaccharomyces pombe (KIN1) (m36060), and soybean (Glycine max) (AF128443). Other serine/threonine kinases tested, which are not directly regulated by calcium or calmodulin, were the DNA damage-induced DUN1 kinase of S. cerevisiae (S43941), human phosphorylase kinase (catalytic subunit [KIHUCT]), and two kinases in the metazoan AGC group (the mitogen- and stress-activated MSK1 kinase of humans, T13149, and the Gallus gallus ribosomal protein S6 kinase, M28488).