TABLE 3.
Hydrolysis of different amides by enantioselective amidases from R. erythropolis MP50 and A. tumefaciens d3a
| Substrate | Structure | Relative activity (%)
|
Enantiomeric ratio
|
||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MP50 | d3b | MP50 | d3b | ||
| 2-Phenylpropionamide | 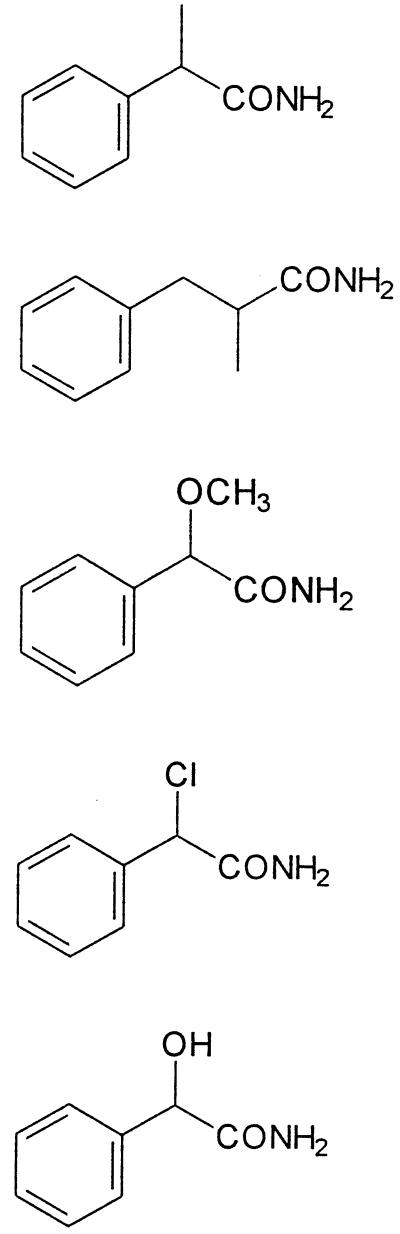 |
100 | 100 | >100 | >100 |
| 2-Methyl-3-phenylpropionamide | 104 ± 21 | 37 | 15 | >100 | |
| 2-Methoxyphenylacetamide | 20 ± 1 | 3 | >100 | 36 | |
| 2-Chlorophenylacetamide | 112 ± 6 | 56 | >100 | >100 | |
| Mandeloamide | 25 ± 6 | 15 | 8 | 6 | |
The reaction mixtures were 0.5 ml and contained 15 μmol of Tris-HCl (pH 7.5), 0.25 μmol of the respective amide, and purified amidase (1.4 to 3.2 mg) from R. erythropolis MP50. The reference data for the amidase from A. tumefaciens d3 were determined in 25 μM Na phosphate or K phosphate buffer (pH 7.4) with cell extracts (0.01 to 0.6 mg) from E. coli JM109 (pST2WT) (60). The specific activities of the purified amidase from strain MP50 and the cell extract from E. coli JM109 pST2WT with 2-phenylpropionamide as substrate were 3.4 ± 0.7 and 0.39 U/mg of protein, respectively. The tests were performed in duplicate, and the standard deviations are given.
Data were taken from a previous report (60), with permission.
