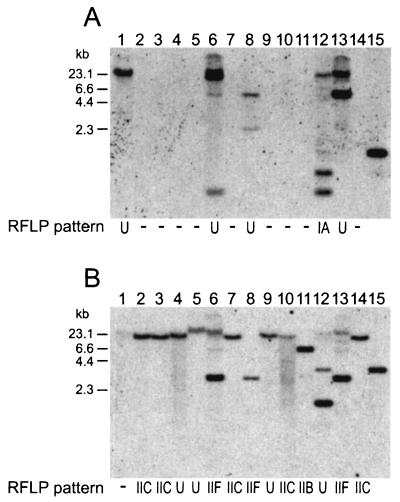
FIG. 3.
Distribution of the form I (cbbL) and form II (cbbM) RubisCO genes among the isolates of purple nonsulfur bacteria as determined by Southern hybridization analyses under high-stringency conditions. EcoRI-digested DNA from a single representative of each genotype and Rhodopseudomonas palustris strain DCP3 was probed with the cbbL (A) and cbbM (B) genes. Lane 1, genotype BiesB3; lane 2, BiesB6; lane 3, BiesB7; lane 4, BiesB8; lane 5, BiesB9; lane 6, BiesB18; lane 7, BiesB10; lane 8, BiesB19; lane 9, BiesB11; lane 10, BiesB12; lane 11, BiesB13; lane 12, BiesB20; lane 13, BiesB21; lane 14, BiesB2; lane 15, Rhodopseudomonas palustris strain DCP3. The RFLP patterns of the cbbL gene are designated as follows: IA, 0.85- and 0.49-kb hybridized fragments; U, either a unique pattern or a hybridized fragment more than 23 kb long; −, no homology. The RFLP patterns of the cbbM gene are designated as follows: IIB, 6.6-kb hybridized fragment; IIC, 15.0-kb hybridized fragment; IIF, 2.8-kb hybridized fragment; U, either a unique pattern or a hybridized fragment more than 23 kb long; −, no homology.