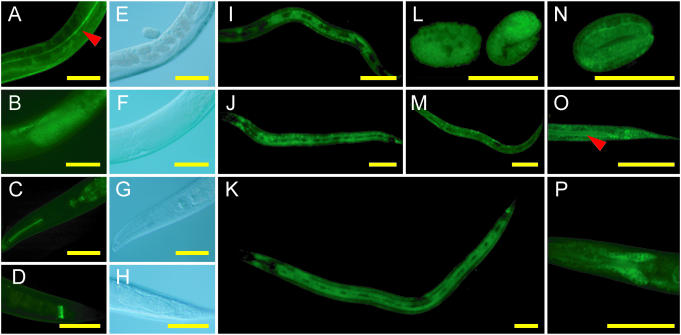
Figure 6.
Representative expression patterns of transgenic worms carrying Gene Catchr-derived transgenes. (A and E) COL-19::GFP; (B and F) GFP::FEM-3; (C, D, G and H) GFP::IFC-2; (I–K) GFP::ROL-6; (L and M) GFP::SKR-7; (N–P) DAF-3::GFP. (L and N) Embryos; (I, M and O) L1 larvae; (J and P) L2 larvae; (K) L4 larva; (A–H) adults. (E–H) DIC images corresponding to GFP fluorescence images (A–D), respectively. (A and E) COL-19::GFP is detected in the cuticle of adult worms, in agreement with previous results (41,68). Note localization to the lateral alae indicated by the red arrowhead (A). (B and F) GFP::FEM-3 accumulation in sperm in adult males. (C and G) GFP::IFC-2 in the pharynx and (D and H) in the posterior of the intestine. In accordance with results obtained by antibody staining (69), we detect GFP::IFC-2 in pharyngeal and intestinal cells at all stages of development (C, D, G and H and data not shown). This represents the first account of ifc-2 expression from a reporter transgene. (I–K) GFP::ROL-6 expression in the hypodermis, excluding the seam cells. (L and M) GFP::SKR-7 is widely expressed in embryos (L), L1 larvae (M) and L2 larvae (not shown). (N–P) DAF-3::GFP is expressed in several tissues including the tail and lumenal surface of the intestine (indicated by the red arrowhead) (O), and the head neurons (P), consistent with results obtained from a translational fusion construct (70). Scale bars represent 50 µm.