Figure 5.
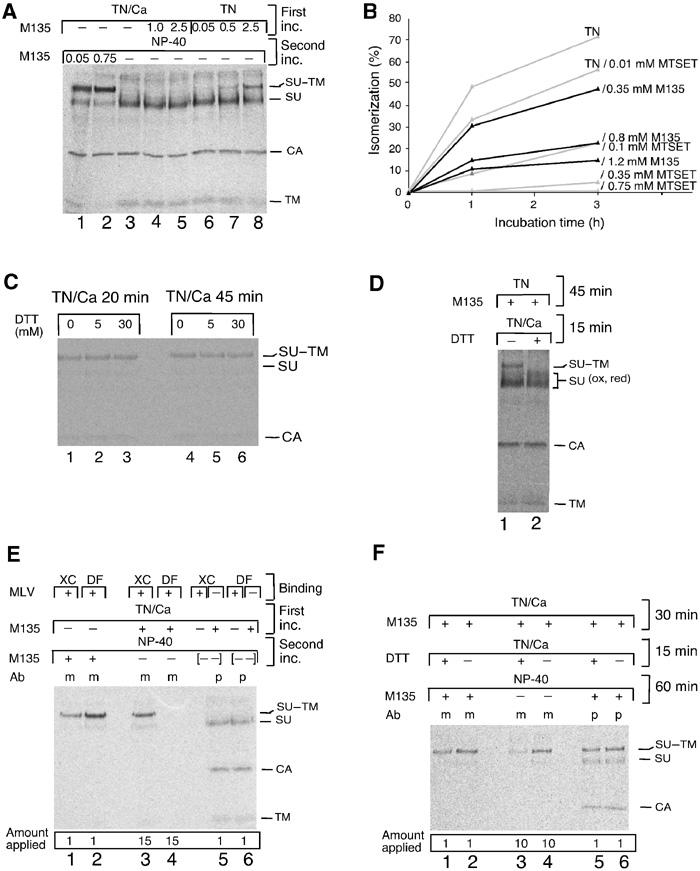
Receptor binding in the presence of alkylator generates an isomerization-arrested Env intermediate. (A) Induction of isomerization exposes CXXC-thiol for alkylation. Mo-MLV was adsorbed to DF-1 cells, washed two times with TN/1.8 mM Ca2+ and incubated for 1 h at 37°C in TN/1.8 mM Ca2+ (lanes 1–5), or washed two times with TN/0.05 mM EDTA and incubated in TN (lanes 6–8), with or without M135 (0.05–2.5 mM) (first inc.). The cells were washed and lysed in NP-40 buffer for 40 min at 30°C with or without alkylator (second inc.). Viral proteins were immunoprecipitated with anti-MLV pAb and analysed by nonreducing SDS–PAGE. (B) Inhibition of TN-induced isomerization by M135 and MTSET in free virus. Mo-MLV in TN was incubated for 0–3 h at 37°C in the presence of 0–1.2 mM alkylator. NEM was added, samples were lysed and viral proteins were analysed as in (A). Isomerization was estimated from the decrease of SU–TM complexes as compared to a control sample incubated in TN with 20 mM NEM and is given in %. (C) The SU–TM disulphide-bond of intact virus is DTT resistant. Mo-MLV was adsorbed to DF-1 cells and incubated for 20 or 45 min at 37°C in TN/1.8 mM Ca2+ with 0–30 mM DTT. NEM was added, samples were lysed and the SU–TM disulphide-bond was analysed as in (A). (D) The SU–TM disulphide-bond of isomerization-induced/M135-arrested Env is DTT sensitive. Mo-MLV was adsorbed to DF-1 cells and incubated first for 45 min at 37°C in TN with 1.5 mM M135 and then, after adding Ca2+ to 1.8 mM, for an additional 15 min with or without 10 mM DTT. Samples were washed, lysed without NEM and disulphide-bonds were analysed as in (A). Note that the M135 isomerization-arrested SU–TM complexes (lane 1) were reduced by DTT (lane 2). (E) Receptor binding exposes CXXC-thiol for alkylation. Mo-MLV was bound to XC or DF-1 cells and incubated for 40 min at 37°C in TN/1.8 mM Ca2+ with or without M135 (1.2 mM) (first inc.). The cultures were washed and lysed in NP-40 buffer for 60 min at 30°C with or without alkylator (second inc.). Viral proteins were immunoprecipitated with mAb 500 (m) or anti-MLV pAb (p) and analysed by nonreducing SDS–PAGE. Samples 5 and 6 are controls where lysates of alkylated XC or DF-1 cells have been mixed ([- -]) with nonalkylated virus–cell samples. The complete isomerization observed indicates that the alkylator has been efficiently removed after the first incubation. Note relative differences between the amounts of samples that have been applied on the gel. (F) Receptor-bound Env, arrested in isomerization by alkylation, is sensitive to SU–TM disulphide-bound reduction. Mo-MLV was bound to XC cells and incubated and analysed as in (E), but including 15 min incubation in TN/1.8 mM Ca2+ with or without 5 mM DTT before incubation with NP-40. Note that SU of cleaved complexes is not seen by mAb 500 (lane 3).
