Figure 7.
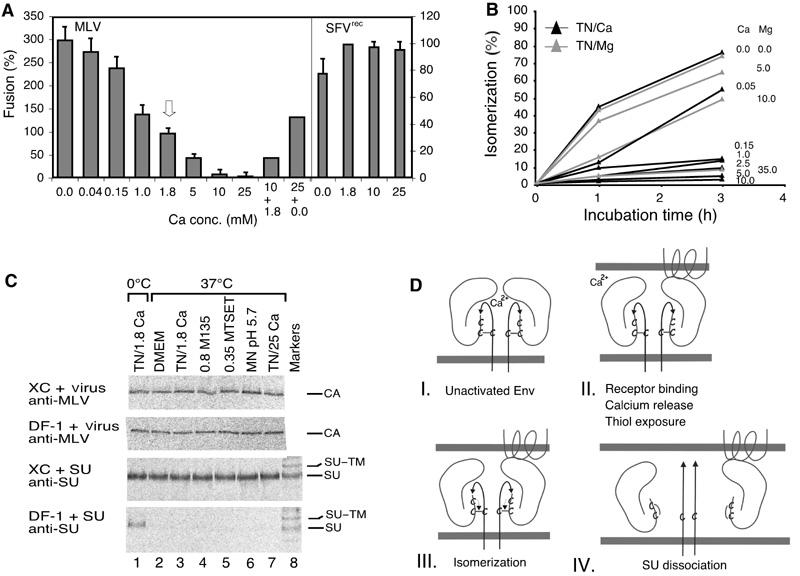
Isomerization induction enhances MLV fusion activity and infectivity. (A) Effect of Ca2+ on Mo-MLV and SFVrec fusion. Mo-MLV was fused to XC cells (left axis) for 15 min in TN, containing 0–25 mM Ca2+. Fusion at control conditions, 1.8 mM Ca2+, is highlighted by an arrow. In some experiments, the virus was first incubated in high Ca2+ (10 or 25 mM) for 15 min and then under control (1.8 mM) or Ca2+-free (0.0 mM) conditions for another 25 min. SFVrec fusions (right axis) were carried out for 10 min in MN, pH 5.6, in the presence of 0–25 mM Ca2+. (B) Effect of Ca2+ and Mg2+ on isomerization kinetics. Virus was taken up into TN containing Ca2+ or Mg2+ as indicated by dialysis and incubated at 37°C for 0–3 h. Isomerization was analysed as in (6H-inset). (C) Effect of alkylators, high Ca2+ and low pH on the specific SU–receptor and the unspecific virus–cell interactions. [35S]Cys-labelled Mo-MLV and accompanying free SU were produced in MOV-3 cells. Part of the culture supernatant was freed from virus by centrifugation and used for SU binding analyses. The unfractionated part was used for virus analyses. Virus and SU were bound to receptor-positive XC and receptor-negative DF-1 cells at 4°C for 1 h and then washed and incubated in control conditions (DMEM or TN/1.8 mM Ca2+), TN/1.8 mM Ca2+/0.8 mM M135, TN/1.8 mM Ca2+/0.35 mM MTSET, MN/pH 5.7/1.8 mM Ca2+ or TN/25 mM Ca2+ at 0°C (lane 1) or 37°C (lanes 2–7) for 15 min. Cell-bound SU or virus were immunoprecipitated with anti-SU or anti-MLV pAb and analysed by nonreducing SDS–PAGE. Note that only the CA band of cell-bound virus is shown. Note also that, in contrast to virus, free SU can only bind to the receptor-positive XC cells, and that alkylators, low pH and high Ca2+ do not significantly affect the specific SU–receptor or the unspecific virus–cell interactions. (D) Schematic model showing how the isomerization of the SU–TM disulphide-bond controls the fusion function in MLV Env. Four steps in the activation pathway (I–IV) are shown. The main events at each step are indicated. Two SU–TM complexes of the trimeric Env are depicted. Each consists of the membrane-anchored TM subunit, with the fusion peptide (arrow), and the peripheral SU subunit. The SU–TM disulphide-bond and the associated CXXC motif in SU are indicated. The target membrane at the top contains a multispanning Env-receptor protein.
