Figure 3.
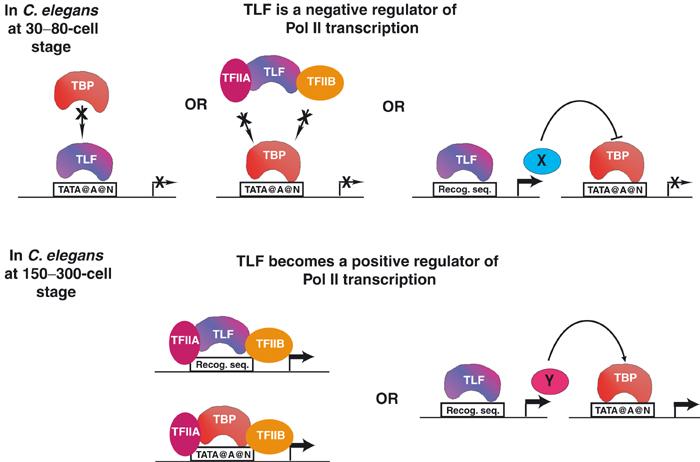
In C. elegans, TLF can function as a negative or a positive regulator of transcription. At the 30–80-cell stage, TLF may function as a repressor, which blocks TBP binding to promoters, or by titrating other GTFs from PIC formation, or by regulating a Pol II repressor factor (X). At the 150–300-cell stage, TLF becomes a positive regulator of Pol II transcription by either forming PICs on promoters where it will find its binding site (Recog. seq.) or by mediating transcription of an essential factor (Y) of Pol II transcription.
