Figure 5.
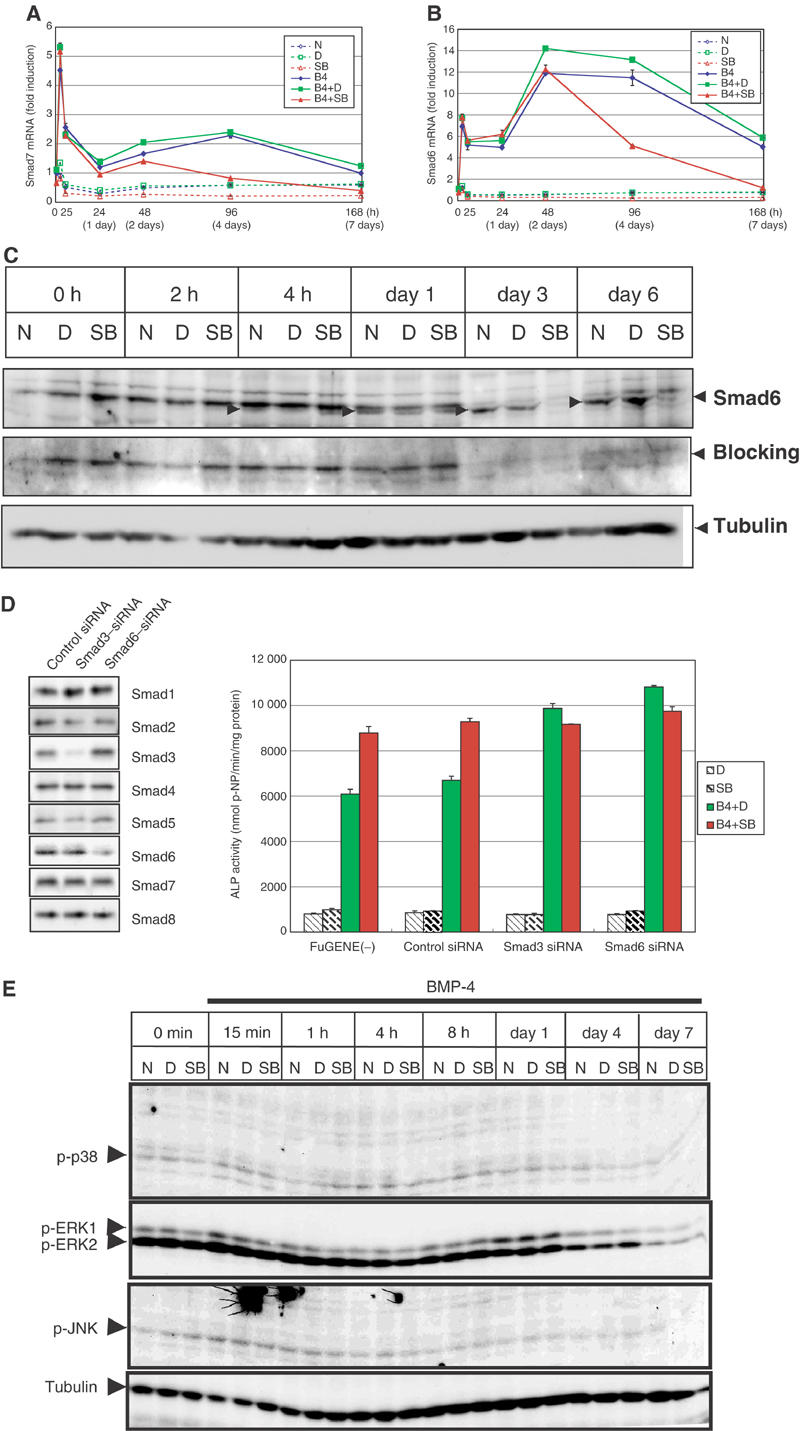
Effects of SB431542 on expression of I-Smads. (A, B) Quantitative RT–PCR for Smad7 gene (Madh7) (A) and Smad6 gene (Madh6) (B) was performed as in Figure 2. (C) Immunoblot analysis for endogenous Smad6. C2C12 cells were pretreated or not with DMSO (0.01%) or SB431542 (1 μM) for 30 min in 5% FBS before stimulation. Cells were stimulated with BMP-4 (50 ng/ml) in combinations with or without DMSO or SB431542. Whole-cell extracts were prepared at indicated time points. Smad6 was detected by anti-Smad6 antiserum (RPR). Bands specifically detected by the antiserum are indicated by arrowheads. Specificity of the bands was confirmed by reblotting of the membrane with blocking of the antiserum with the peptide used for immunization. The bands for tubulin are shown as a loading control. (D) Effects of the Smad3 and Smaf6 siRNA on BMP-4-induced osteoblastic differentiation of C2C12 cells. As the effects of siRNA were transient, C2C12 cells were treated with 150 ng/ml BMP-4 and ALP activity was determined at day 6. Expression levels of each Smad protein in the presence of control, Smad3, or Smad6 siRNA were determined by immunoblotting using transfected C2C12 cells (left panel). (E) Phosphorylation of MAPKs during osteoblastic differentiation. C2C12 cells were treated as in Figure 4A, and subjected to immunoblotting using anti-phospho-p38, anti-phospho-ERK1/2, or anti-phospho-JNK antibodies. The bands for tubulin are shown as a loading control.
