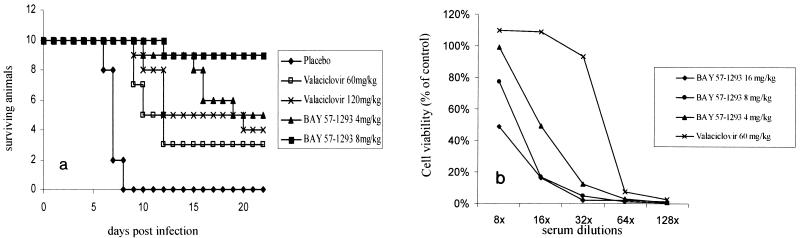
FIG. 5.
(a) Comparison of BAY 57-1293 with valacyclovir in the murine lethal challenge model using once-daily dosing. Mice were infected intranasally with a potentially lethal dose of HSV-2MS and were treated orally with BAY 57-1293 or valacyclovir once daily from day 0 to day 4 postinfection at the indicated doses. Ten animals from each group were used. Infected mice were inspected daily, and a survival curve was recorded. Treatment with 8 mg of BAY 57-1293 per kg was significantly superior to treatment with 120 mg of valacyclovir per kg under once-daily-dosing conditions (P = 0.02 by the unpaired two-tailed t test). (b) Neutralizing anti-HSV antibody titers. Animals treated with the indicated doses as described above for panel a were killed 4 weeks after infection, and their serum was analyzed for HSV-neutralizing activity, as described in Materials and Methods. Antibody production was decreased in BAY 57-1293-treated animals compared with that in valacyclovir-treated animals. Average values for three to six animals per group are shown.