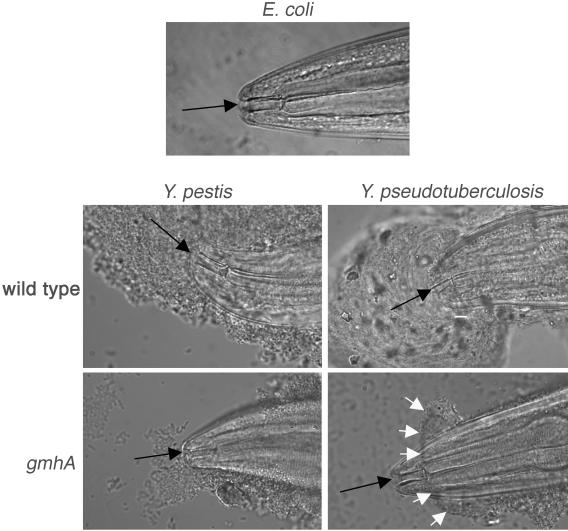
FIG. 2.
Biofilms on C. elegans made by Yersinia wild-type and gmhA mutant strains. A nematode grown on E. coli food strain OP50 is shown for comparison. Black arrows, mouth. Wild-type Y. pestis and Y. pseudotuberculosis biofilms cover the mouth completely and block feeding. Most Y. pestis gmhA biofilms fail to attach to the mouth (not shown), but a few are as shown, accounting for the 2% of C. elegans animals that fail to grow normally on this strain (Fig. 1). Y. pseudotuberculosis gmhA biofilms attach to the side of the head posterior to the mouth; white arrows mark the forward edge of the biofilm.