Figure 6.
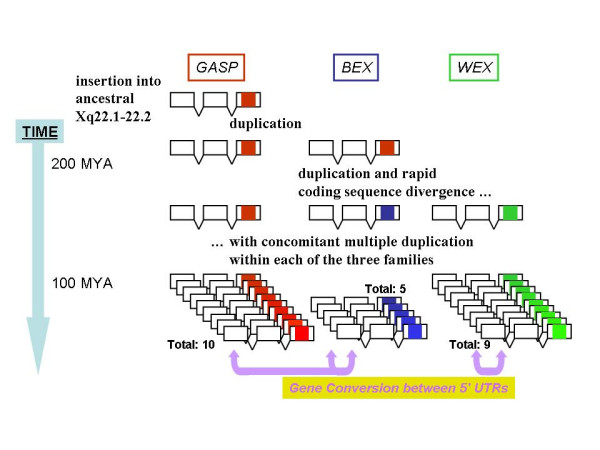
Proposed evolutionary events leading to BEX, WEX and GASP genes on human chromosome Xq22.1-q22.2. BEX and WEX genes arise due to duplication of a GASP-like gene early in eutherian mammalian history. These genes undergo multiple duplication events thereafter, but prior to the divergence of human and dog lineages. Multiple events of gene conversion, either between 5' UTRs or between coding sequences (Additional file 1), occur with the remaining coding sequence diverging rapidly due to relaxed selective constraints and/or adaptive evolution.
