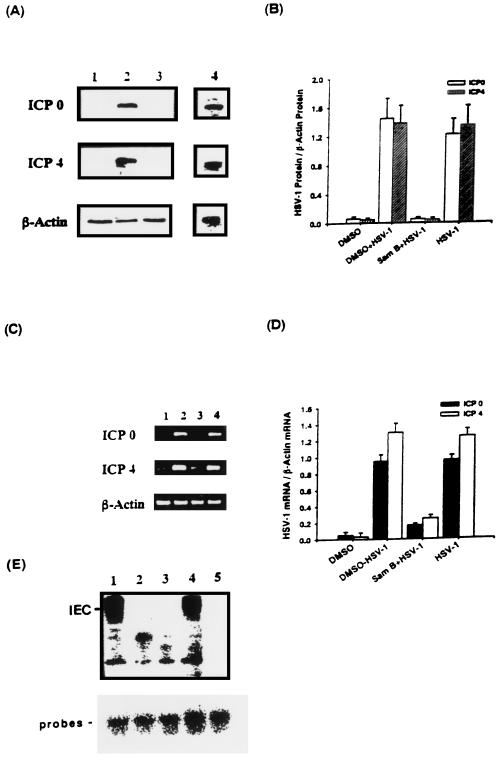
FIG. 9.
Effects of Sam B on HSV-1 ICP0 and ICP4 gene expression and formation of IEC in Vero cells detected by Western blotting, RT-PCR, and EMSA, respectively. Vero cells (5 × 106) were infected with HSV-1 (MOI, 3) or were not infected in the presence or absence of Sam B (25 μM). (A) Lysates (20 μg of protein) were collected at 4 h p.i. and run on an SDS-10% PAGE gel and analyzed by immunoblotting with an anti-ICP0 or -ICP4 antibody. (C) Total cellular RNA was isolated from Vero cells at 4 h p.i. and analyzed by RT-PCR. Lane 1, uninfected Vero cells; lanes 2 and 4, HSV-1-infected cells treated with or without DMSO; lane 3, infected cells treated with Sam B. (B and D) Bar graphs indicating the ratio of ICP0 or ICP4 to β-actin proteins or mRNAs. Each bar represents the mean of three independent experiments. (E) EMSA was performed as described in Materials and Methods. Nuclear extracts from HSV-1-infected (lanes 1 and 4) or uninfected Vero cells (lane 3) were incubated with a 32P-end-labeled GARAT probe. The effects of Sam B on the formation of IEC in virus-infected nuclear extracts pretreated with 25 μM Sam B for 5 min and then mixed with the probes (lane 2) were detected. Lane 5, results of adding a 50-fold excess of unlabeled probe to the reaction mixture.