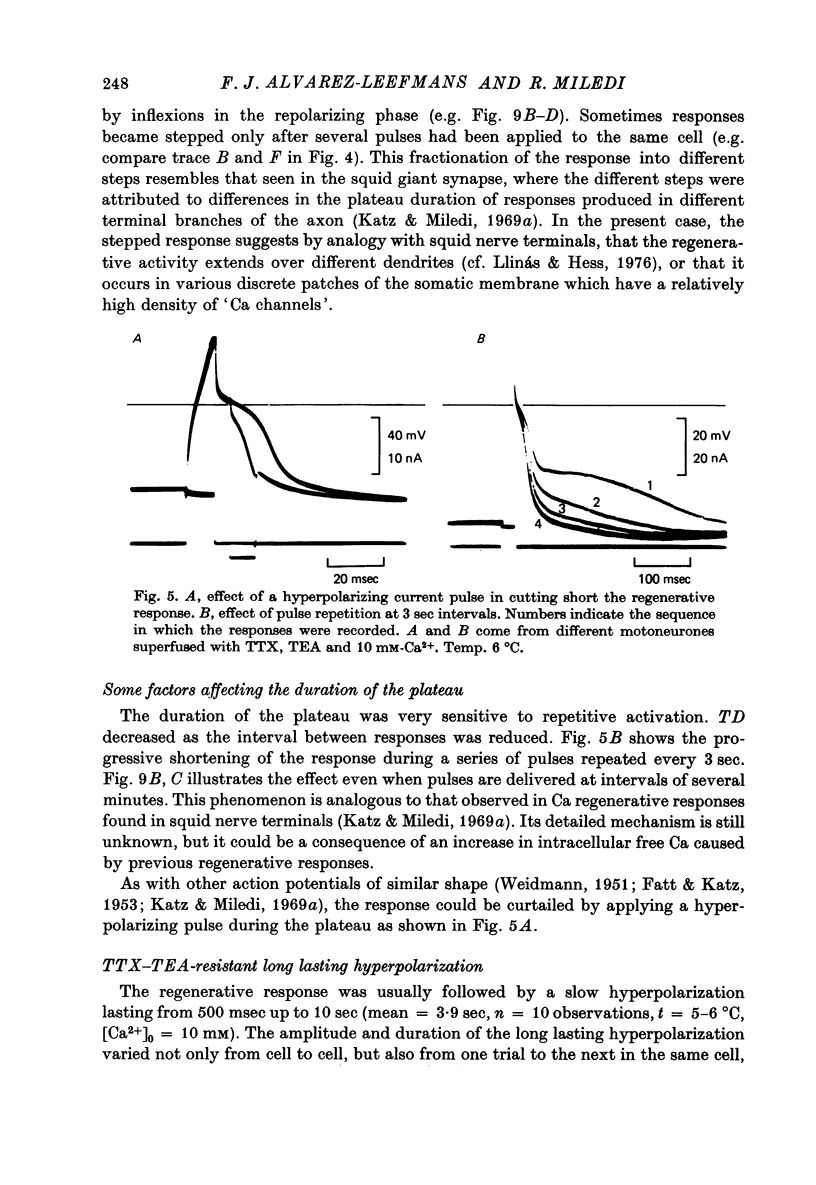
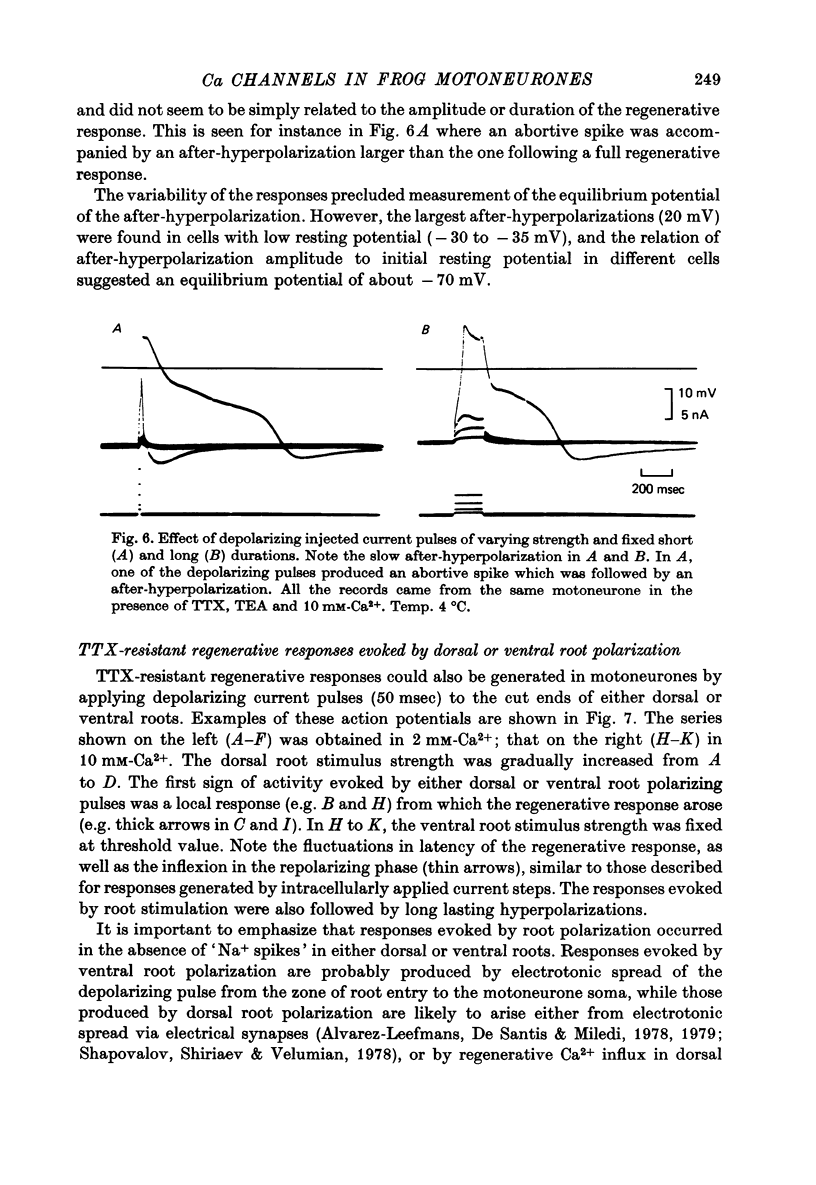
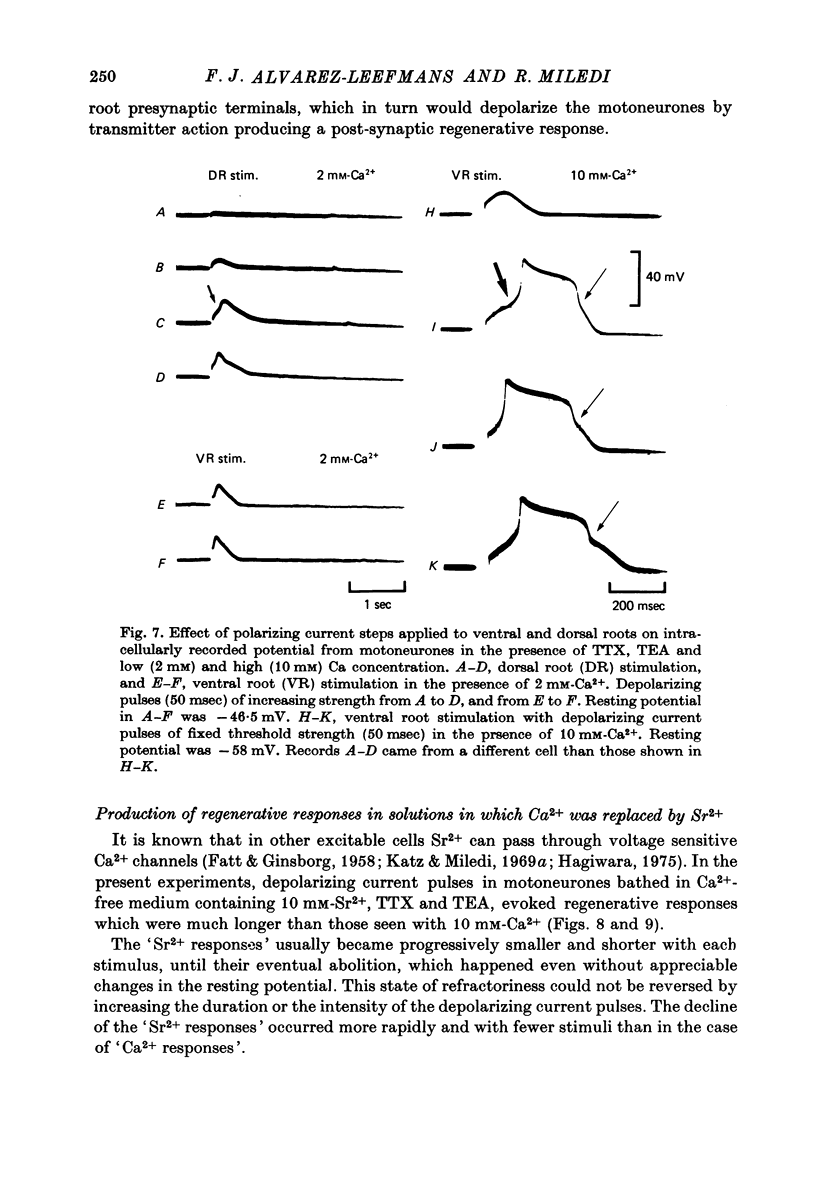
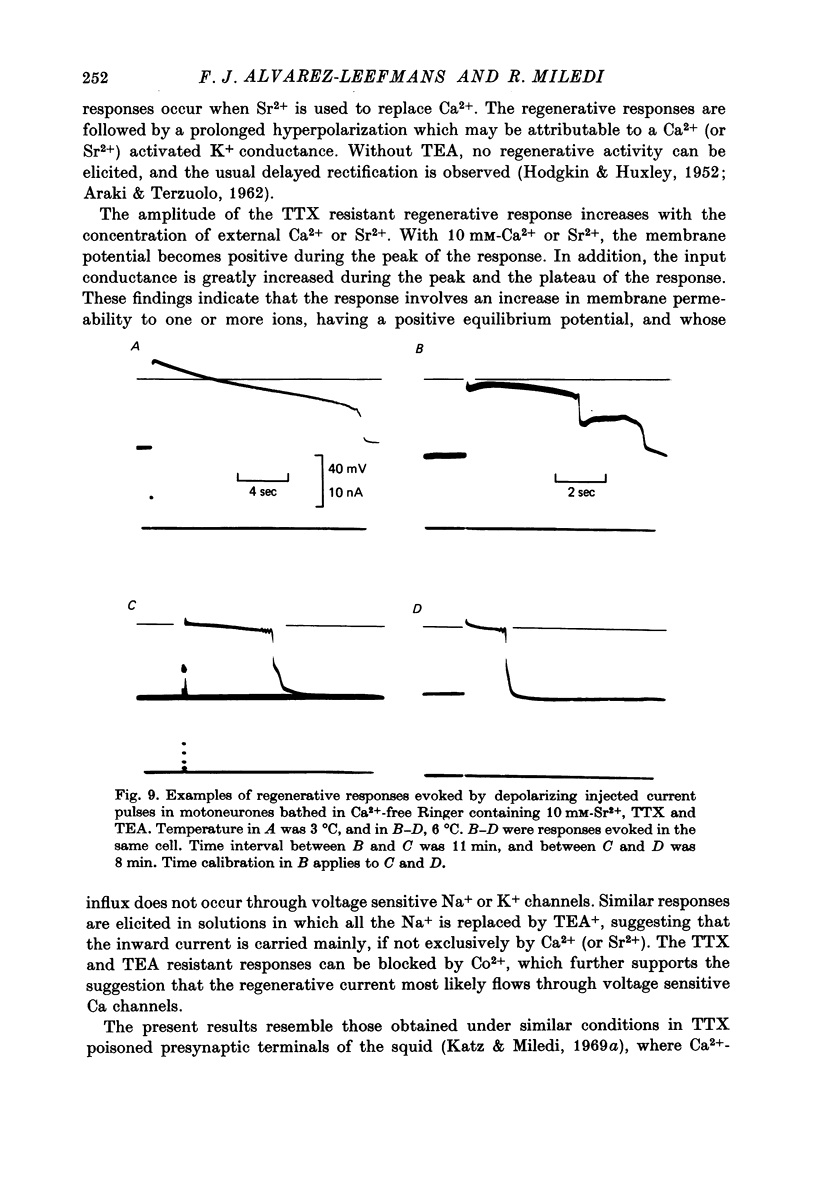
Abstract
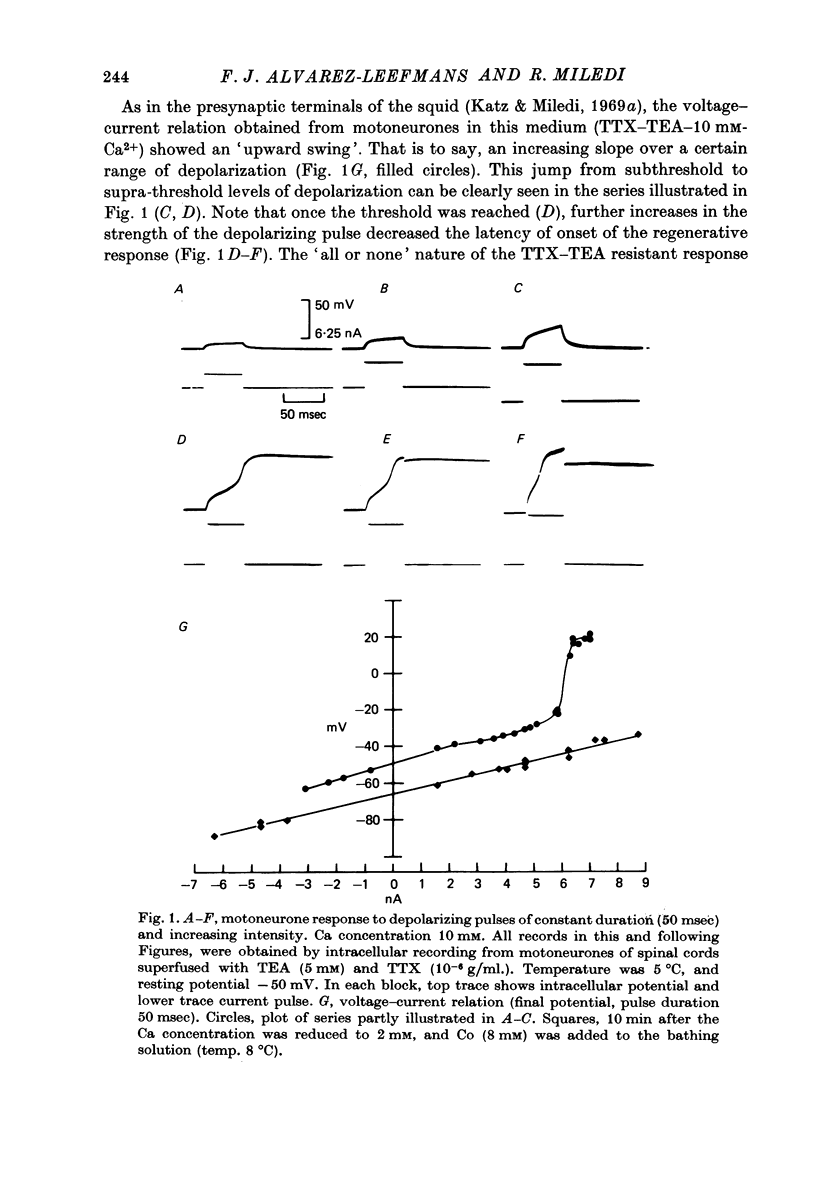
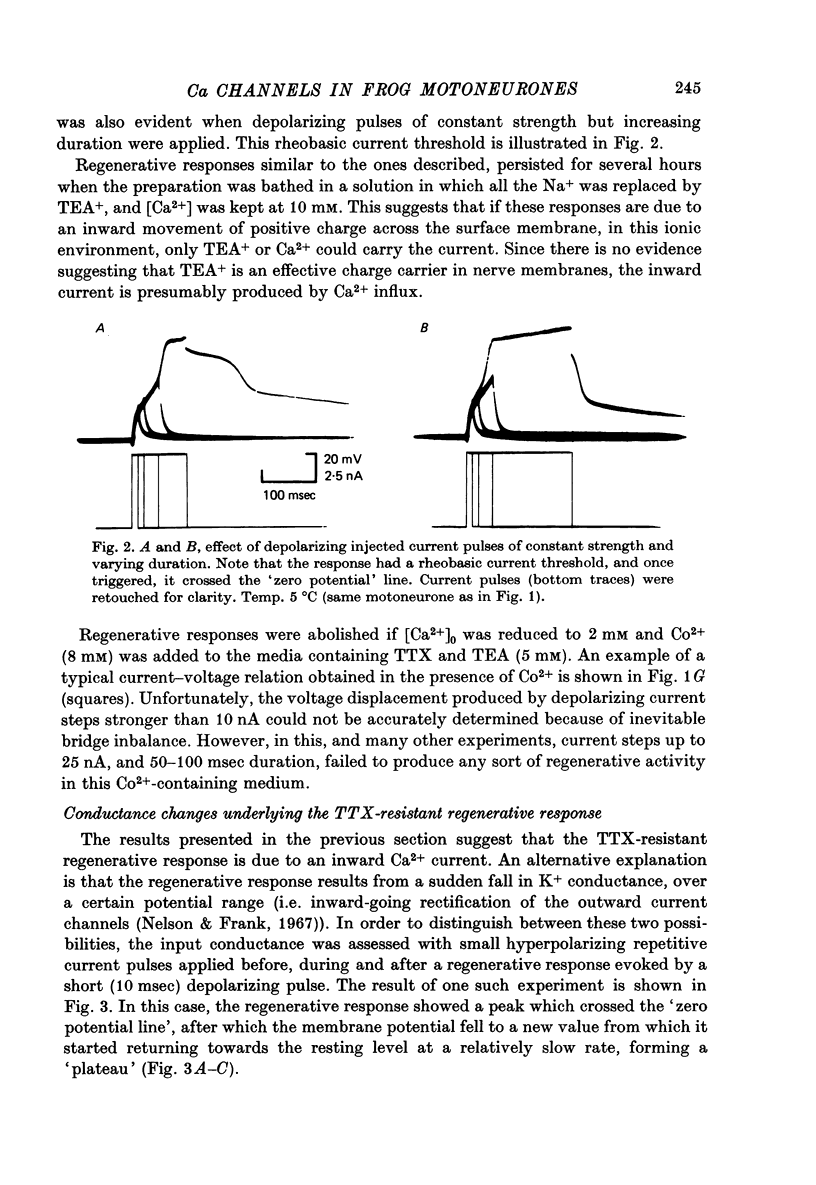
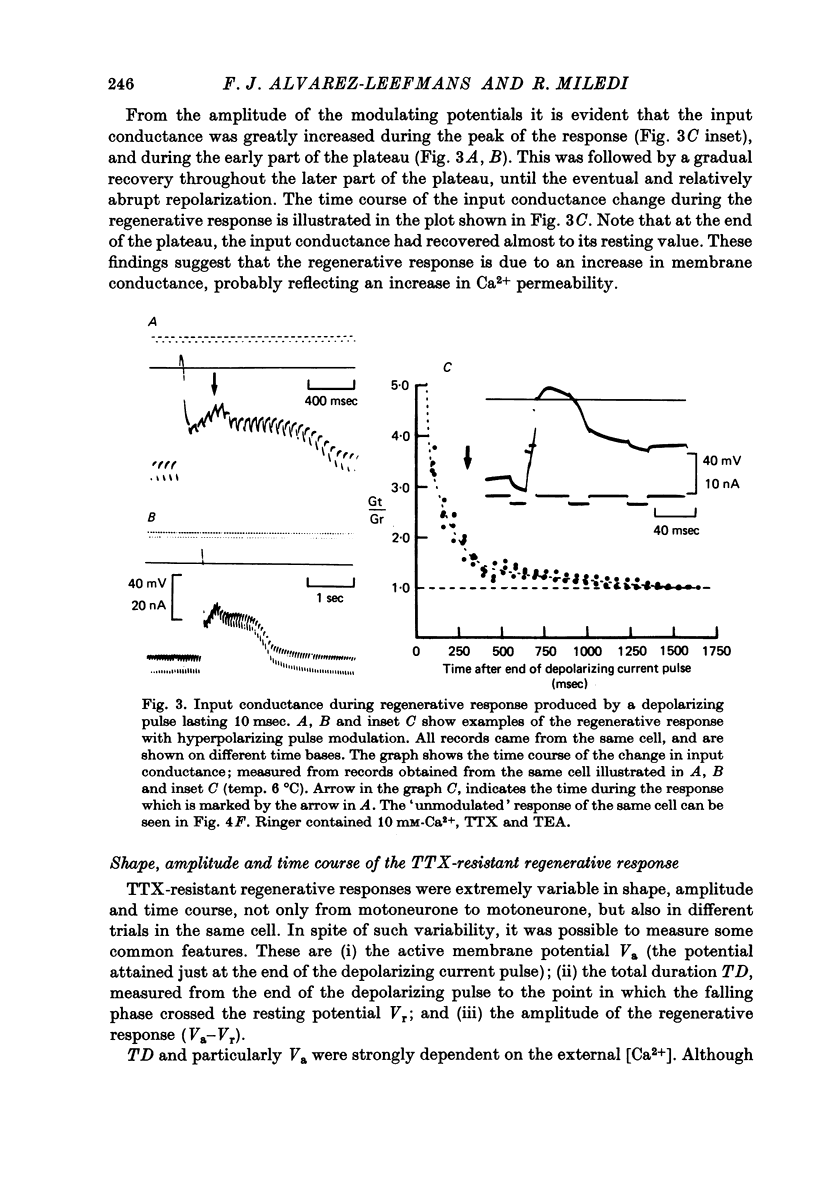
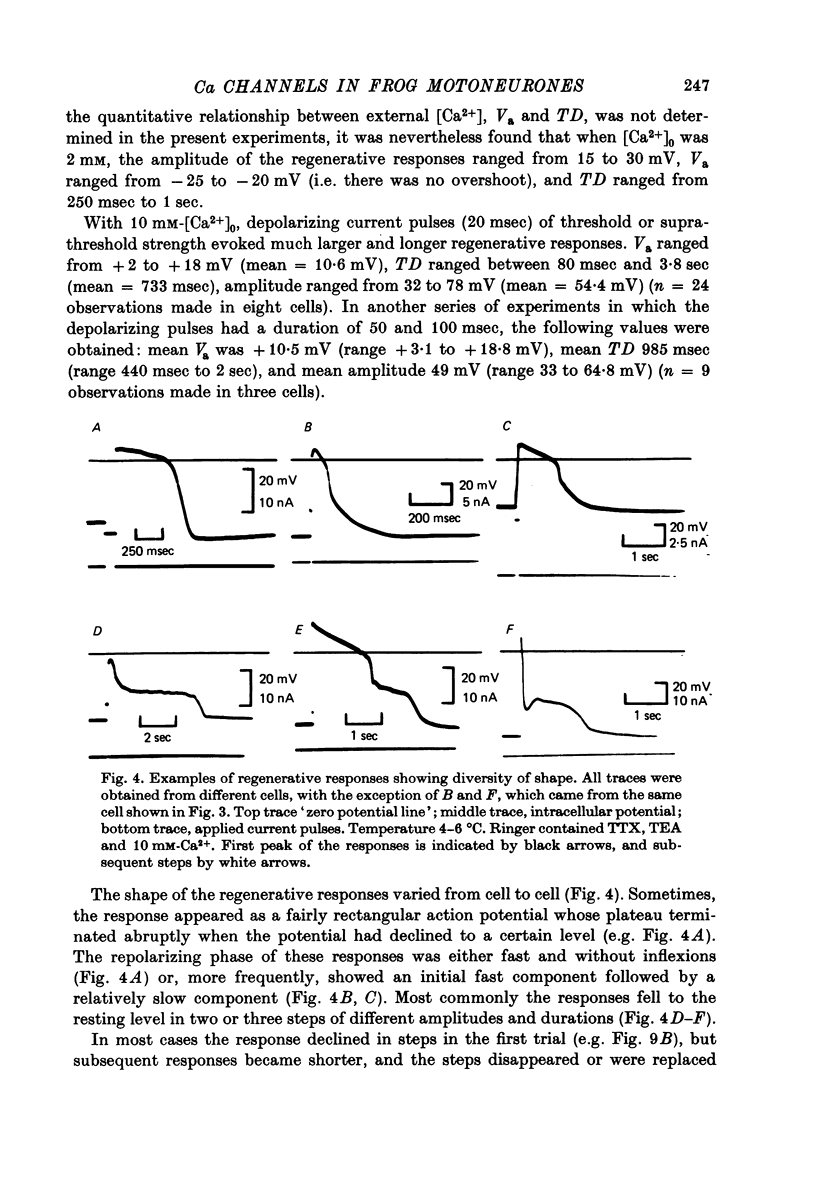
1. The electrical properties of motoneurone membrane were investigated in the isolated and hemisected spinal cord of frogs, using intracellular recording techniques. 2. TTX (1 x 10(-6) g/ml.) blocked action potentials produced either by intracellular depolarizing current pulses or ventral root stimuli. Voltage--current relations from these cells showed a diminishing slope for depolarizing current pulses of increasing intensity. 3. If TEA (5--10 mM) was added to the media containing TTX, intracellular depolarizing pulses elicited prolonged regenerative depolarizations characterized by a peak of variable amplitude and a repolarizing phase preceded by a prolonged plateau of variable duration. 4. During the plateau of the response, the membrane conductance was increased above its resting value. 5. The response was shortened during repetitive stimulation and could be curtailed by applying a hyperpolarizing pulse during the plateau. 6. The response depended on the presence of external Ca2+ and increased in size and duration with increasing Ca2+ concentration. Sr2+ substituted effectively for Ca2+. Sr2+-dependent responses were considerably longer than the Ca2+-dependent ones. Ca2+ or Sr2+ dependent responses persisted in Na+-free media containing isotonic TEA, and were abolished by addition of Co2+. 7. Ca2+ or Sr2+-dependent regenerative responses were followed by a hyperpolarization which could last several seconds. The current responsible for this after-hyperpolarization was TTX and TEA resistant. 8. It is concluded that the TTX-resistant regenerative response is probably generated in the soma-dendritic membrane, and is due to influx of Ca2+ or Sr2+ through voltage sensitive channels different to those through which Na+ permeates during generation of 'normal' action potentials. In addition it is shown that the hyperpolarization following 'Ca spikes', and which might be due to an increase in K+ conductance can also be triggered by Sr2+.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ARAKI T., OTANI T., FURUKAWA T. The electrical activities of single motoneurones in toad's spinal cord, recorded with intracellular electrodes. Jpn J Physiol. 1953 Dec 15;3(4):254–267. doi: 10.2170/jjphysiol.3.254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ARAKI T., TERZUOLO C. A. Membrane currents in spinal motoneurons associated with the action potential and synaptic activity. J Neurophysiol. 1962 Nov;25:772–789. doi: 10.1152/jn.1962.25.6.772. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ARMSTRONG C. M., BINSTOCK L. ANOMALOUS RECTIFICATION IN THE SQUID GIANT AXON INJECTED WITH TETRAETHYLAMMONIUM CHLORIDE. J Gen Physiol. 1965 May;48:859–872. doi: 10.1085/jgp.48.5.859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alvarez-Leefmans F. J., De Santis A., Miledi R. Effects of some divalent cations on synaptic transmission in frog spinal neurones. J Physiol. 1979 Sep;294:387–406. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012936. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alvarez-Leefmans F. J., Miledi R. Voltage sensitive calcium channels in frog spinal motoneurones [proceedings]. J Physiol. 1979 Oct;295:81P–82P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alvarez-Leefmans F. J., de Santis A., Miledi R. Possible electrotonic coupling between dorsal root afferents and frog spinal motoneurones [proceedings]. J Physiol. 1978 Dec;285:63P–63P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BROCK L. G., COOMBS J. S., ECCLES J. C. The recording of potentials from motoneurones with an intracellular electrode. J Physiol. 1952 Aug;117(4):431–460. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker P. F., Hodgkin A. L., Ridgway E. B. Depolarization and calcium entry in squid giant axons. J Physiol. 1971 Nov;218(3):709–755. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker P. F., Meves H., Ridgway E. B. Calcium entry in response to maintained depolarization of squid axons. J Physiol. 1973 Jun;231(3):527–548. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldissera F., Gustafsson B. Firing behaviour of a neurone model based on the afterhyperpolarization conductance time course. First interval firing. Acta Physiol Scand. 1974 Aug;91(4):528–544. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1974.tb05708.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett E. F., Barret J. N. Separation of two voltage-sensitive potassium currents, and demonstration of a tetrodotoxin-resistant calcium current in frog motoneurones. J Physiol. 1976 Mar;255(3):737–774. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011306. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brehm P., Eckert R. Calcium entry leads to inactivation of calcium channel in Paramecium. Science. 1978 Dec 15;202(4373):1203–1206. doi: 10.1126/science.103199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COOMBS J. S., ECCLES J. C., FATT P. The electrical properties of the motoneurone membrane. J Physiol. 1955 Nov 28;130(2):291–325. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1955.sp005411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colomo F., Erulkar S. D. Miniature synaptic potentials at frog spinal neurones in the presence of tertodotoxin. J Physiol. 1968 Nov;199(1):205–221. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connor J. A. Calcium current in molluscan neurones: measurement under conditions which maximize its visibility. J Physiol. 1979 Jan;286:41–60. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012606. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dichter M. A., Fischbach G. D. The action potential of chick dorsal root ganglion neurones maintained in cell culture. J Physiol. 1977 May;267(2):281–298. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dipolo R., Requena J., Brinley F. J., Jr, Mullins L. J., Scarpa A., Tiffert T. Ionized calcium concentrations in squid axons. J Gen Physiol. 1976 Apr;67(4):433–467. doi: 10.1085/jgp.67.4.433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckert R., Lux H. D. A voltage-sensitive persistent calcium conductance in neuronal somata of Helix. J Physiol. 1976 Jan;254(1):129–151. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FATT P., GINSBORG B. L. The ionic requirements for the production of action potentials in crustacean muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1958 Aug 6;142(3):516–543. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1958.sp006034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FATT P., KATZ B. The electrical properties of crustacean muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1953 Apr 28;120(1-2):171–204. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1953.sp004884. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman A. L., Hermann A. Internal effects of divalent cations on potassium permeability in molluscan neurones. J Physiol. 1979 Nov;296:393–410. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp013012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HUXLEY A. F. A quantitative description of membrane current and its application to conduction and excitation in nerve. J Physiol. 1952 Aug;117(4):500–544. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004764. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagiwara S. Ca-dependent action potential. Membranes. 1975;3:359–381. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hille B. The selective inhibition of delayed potassium currents in nerve by tetraethylammonium ion. J Gen Physiol. 1967 May;50(5):1287–1302. doi: 10.1085/jgp.50.5.1287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KATZ B., MILEDI R. A STUDY OF SPONTANEOUS MINIATURE POTENTIALS IN SPINAL MOTONEURONES. J Physiol. 1963 Sep;168:389–422. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz B., Miledi R. A study of synaptic transmission in the absence of nerve impulses. J Physiol. 1967 Sep;192(2):407–436. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz B., Miledi R. Spontaneous and evoked activity of motor nerve endings in calcium Ringer. J Physiol. 1969 Aug;203(3):689–706. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz B., Miledi R. Tetrodotoxin-resistant electric activity in presynaptic terminals. J Physiol. 1969 Aug;203(2):459–487. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008875. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kernell D., Sjöholm H. Repetitive impulse firing: comparisons between neurone models based on 'voltage clamp equations' and spinal motoneurones. Acta Physiol Scand. 1973 Jan;87(1):40–56. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1973.tb05364.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleinhaus A. L., Prichard J. W. Calcium dependent action potentials produced in leech Retzius cells by tetraethylammonium chloride. J Physiol. 1975 Mar;246(2):351–369. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp010894. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koketsu K., Nishi S. Calcium and action potentials of bullfrog sympathetic ganglion cells. J Gen Physiol. 1969 May;53(5):608–623. doi: 10.1085/jgp.53.5.608. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kostyuk P. G., Krishtal O. A., Shakhovalov Y. A. Separation of sodium and calcium currents in the somatic membrane of mollusc neurones. J Physiol. 1977 Sep;270(3):545–568. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krnjević K., Puil E., Werman R. EGTA and motoneuronal after-potentials. J Physiol. 1978 Feb;275:199–223. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012186. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Llinás R., Hess R. Tetrodotoxin-resistant dendritic spikes in avian Purkinje cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jul;73(7):2520–2523. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.7.2520. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Llinás R., Steinberg I. Z., Walton K. Presynaptic calcium currents and their relation to synaptic transmission: voltage clamp study in squid giant synapse and theoretical model for the calcium gate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Aug;73(8):2918–2922. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.8.2918. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McAfee D. A., Yarowsky P. J. Calcium-dependent potentials in the mammalian sympathetic neurone. J Physiol. 1979 May;290(2):507–523. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meech R. W. Calcium-dependent potassium activation in nervous tissues. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1978;7:1–18. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.07.060178.000245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meech R. W. Intracellular calcium injection causes increased potassium conductance in Aplysia nerve cells. Comp Biochem Physiol A Comp Physiol. 1972 Jun 1;42(2):493–499. doi: 10.1016/0300-9629(72)90128-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meech R. W., Standen N. B. Potassium activation in Helix aspersa neurones under voltage clamp: a component mediated by calcium influx. J Physiol. 1975 Jul;249(2):211–239. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meves H., Vogel W. Calcium inward currents in internally perfused giant axons. J Physiol. 1973 Nov;235(1):225–265. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010386. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moolenaar W. H., Spector I. The calcium action potential and a prolonged calcium dependent after-hyperpolarization in mouse neuroblastoma cells. J Physiol. 1979 Jul;292:297–306. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NARAHASHI T., MOORE J. W., SCOTT W. R. TETRODOTOXIN BLOCKAGE OF SODIUM CONDUCTANCE INCREASE IN LOBSTER GIANT AXONS. J Gen Physiol. 1964 May;47:965–974. doi: 10.1085/jgp.47.5.965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson P. G., Frank K. Anomalous rectification in cat spinal motoneurons and effect of polarizing currents on excitatory postsynaptic potential. J Neurophysiol. 1967 Sep;30(5):1097–1113. doi: 10.1152/jn.1967.30.5.1097. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reuter H. Divalent cations as charge carriers in excitable membranes. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1973;26:1–43. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(73)90016-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reuter H., Scholz H. A study of the ion selectivity and the kinetic properties of the calcium dependent slow inward current in mammalian cardiac muscle. J Physiol. 1977 Jan;264(1):17–47. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011656. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross W. N., Stuart A. E. Voltage sensitive calcium channels in the presynaptic terminals of a decrementally conducting photoreceptor. J Physiol. 1978 Jan;274:173–191. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartzkroin P. A., Slawsky M. Probable calcium spikes in hippocampal neurons. Brain Res. 1977 Oct 21;135(1):157–161. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)91060-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapovalov A. I., Shiriaev B. I., Velumian A. A. Mechanisms of post-synaptic excitation in amphibian motoneurones. J Physiol. 1978 Jun;279:437–455. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Standen N. B. Calcium and sodium ions as charge carriers in the action potential of an identified snail neurone. J Physiol. 1975 Jul;249(2):241–252. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson S. H. Three pharmacologically distinct potassium channels in molluscan neurones. J Physiol. 1977 Feb;265(2):465–488. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tillotson D. Inactivation of Ca conductance dependent on entry of Ca ions in molluscan neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1497–1500. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WASHIZU Y. The effect of TEA on the electrical activities of spinal motoneurons. Jpn J Physiol. 1959 Sep 15;9:311–321. doi: 10.2170/jjphysiol.9.311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEIDMANN S. Effect of current flow on the membrane potential of cardiac muscle. J Physiol. 1951 Oct 29;115(2):227–236. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1951.sp004667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


