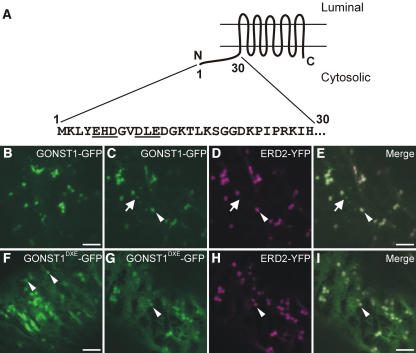
Figure 1.
A Diacidic Motif in the N-Terminal Cytosolic Domain of GONST1 Influences Its ER Export.
(A) Scheme of the topology of GONST1, with the sequence of the 30 N-terminal amino acids. Note the EHD and DLE motifs (underlined).
(B) GONST1-GFP localizes to punctate structures in tobacco leaf epidermal cells.
(C) to (E) The larger GONST1-labeled structures colocalize with ERD2-YFP (arrowheads), whereas the smaller structures are not labeled by ERD2-YFP (arrows).
(F) Mutation of DLE to GLA in GONST1 results in impaired ER export. Transport of GONST1DXE-GFP out of the ER is reduced compared with that of the wild-type protein. Note the increase in ER staining, although some punctate structures remain visible (arrowheads).
(G) to (I) Coexpression of GONST1DXE-GFP (G) with ERD2-YFP (H) confirms that the larger punctate structures labeled by GONST1DXE-GFP are Golgi bodies (arrowheads). Note the colocalization of the two fluorochromes on dots in the merged image (I).
Bars = 5 μm.