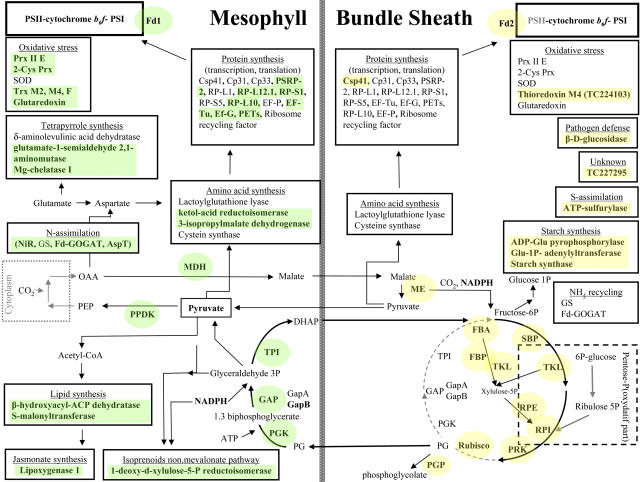
Figure 10.
Overview of the Distribution of Different Chloroplast Functions over BS and M Chloroplasts.
The major metabolic pathways and associated proteins are listed, with some examples of other pathways. The proteins with differential accumulation are indicated in bold and are colored. General metabolic pathways are schematically indicated. Abbreviations are as follows: peroxiredoxines (Prx), superoxide dismutase (SOD), thioredoxins (Trx), magnesium chelatase (Mg-chelatase), nitrite reductase (NiR), glutamine synthase (GS), ferredoxin dependent glutamate synthase (Fd-GOGAT), aspartate transaminase (AspT), nucleic acid binding proteins (Cp33, Cp31), plastid specific ribosomal protein (PSRP), ribosomal protein (RP), polyprotein of Ef-Ts (PETs), elongation factors (Ef), glyceraldehyde dehydrogenase (GAP), fructose 1,6-biphosphatase (FBP), sedoheptulose-1,7-bisphosphatase (SBP), transketolase (TKL), ribose-5P-isomerase (RPI), phosphoglycerate kinase (PGK), triose phosphate isomerase (TPI), dihydroxyacetone (DHAP), phosphoglycerate (PG), ferredoxin (Fd), oxaloacetate (OAA), phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) and glucose (Glu).