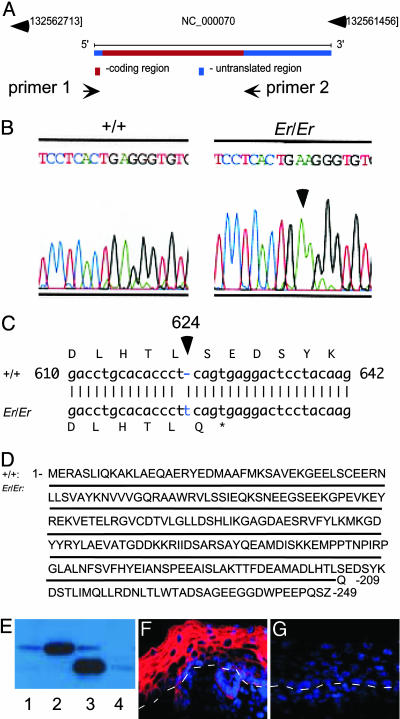
Fig. 3.
A-T pair insertion at nucleotide 624 of the14-3-3σ ORF resulted in a truncated form of protein lacking the C-terminal 40 amino acids. (A) Schematic view of the Sfn gene locus. The PCR primers 1 and 2 were designed to amplify the coding region of 14-3-3σ from genomic DNA. (B and C) Sequence comparison of PCR-amplified fragments from Er/Er and WT (+/+) control shows an A-T pair insertion at nucleotide 624 of the 14-3-3σ ORF. (D) WT 14-3-3σ sequence is shown on top. The mutation produced a truncated isoform of the 14-3-3σ lacking the C-terminal 40 amino acids. The solid line represents the same amino acid sequence in the mutant 14-3-3σ, with the last amino acid residue, Gln, in the place of Ser-209 before the end. (E) Expression of the WT 14-3-3σ ORF in the WT keratinocytes produced a full-length 14-3-3σ of 28 kDa (lane 2, compare with endogenous WT protein in lane 1). In contrast, expression of a mutant form of the 14-3-3σ isolated from Er/Er genomic DNA in the WT keratinocytes generated a truncated isoform of the 14-3-3σ protein with molecular mass of 24 kDa (lane 3, compare with Er/Er mutant endogenous 14-3-3σ in lane 4). (F and G) Immunohistochemical staining of the sagittal sections of the dorsal skins from the WT (F) and Er/Er (G) E18.5 embryos with an antibody specifically recognizing the C terminus of the 14-3-3σ. Positive cells are stained red. Nuclei stained with DAPI are purple. The white dashed lines represent the dermal–epidermal border.