Figure 5.
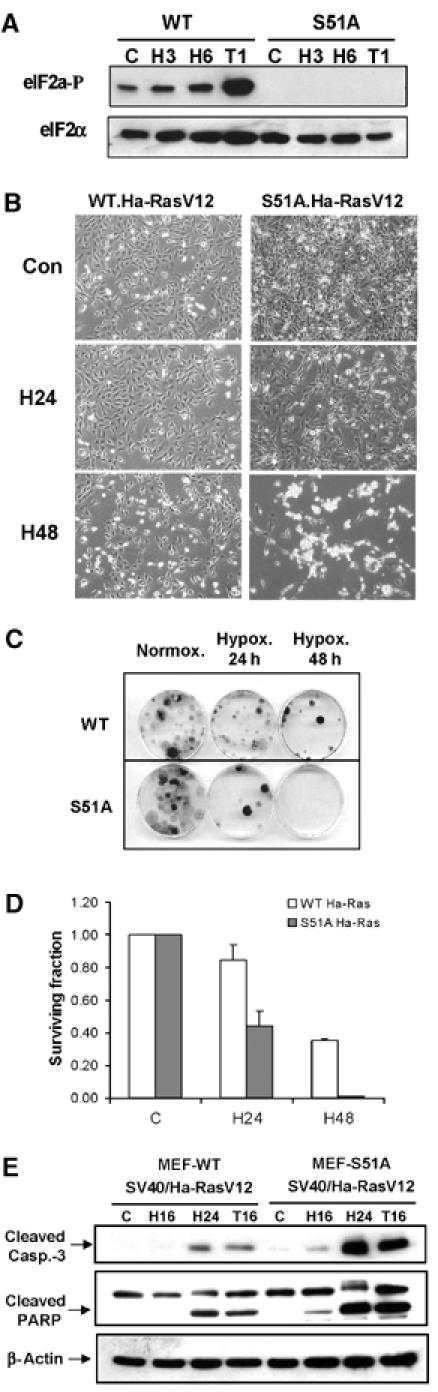
MEFs with nonphosphorylatable eIF2α mutant are more sensitive to extreme hypoxia than WT MEFs. (A) WT and S51A MEFs were exposed to ⩽0.02% O2 or treated with 1 μM thapsigargin before immunoblotting with anti-phospho-eIF2α or anti-total-eIF2α antibodies. (B) WT and S51A MEFs transformed with SV40/Ha-RasV12 were exposed to extreme hypoxia (⩽0.02% O2) and then photographed using phase-contrast microscopy. (C) Reduced clonogenic survival of S51A MEFs after hypoxia compared to WT MEFs. (D) Reduced survival of S51A MEFs after hypoxia compared to WT MEFs, as measured by clonogenic survival assay. Cells were treated as in (C). Experiments were performed in triplicate and error bars represent standard errors. (E) WT and S51A MEFS transformed with SV40/Ha-RasV12 were exposed to hypoxia or treated with 500 nM thapsigargin before immunoblotting for cleaved caspase-3, PARP or β-actin.
