Figure 2.
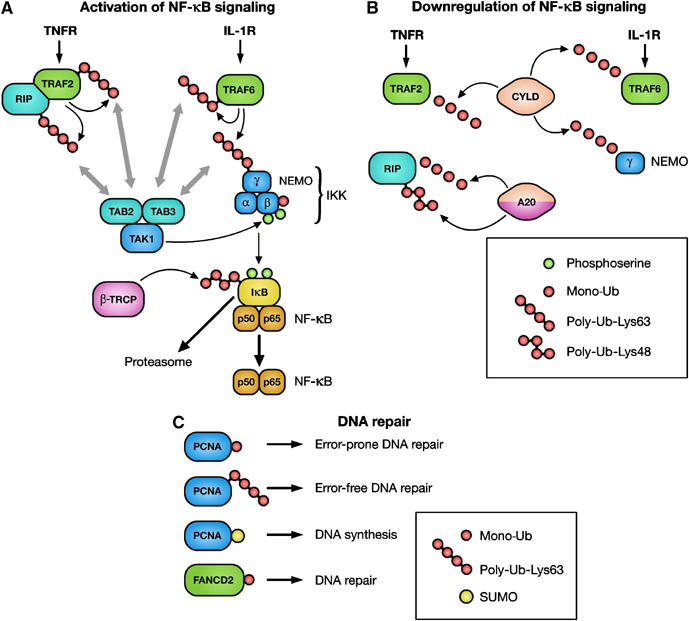
Ub in the regulation of NF-κB signaling and DNA repair. (A) Activation of the Ub ligases TRAF2 and TRAF6 leads to the modification of TRAF2, TRAF6, RIP and NEMO with UbLys63 chains. TAK1 is thought to be recruited to these proteins via TAB2/3, which harbor UBDs. Binding of TAB2/3 to Ub is required for the activation of TAK1, which in turn activates IKK. Serine phosphorylation of IKKβ triggers its monoubiquitylation. Once activated, IKK mediates serine phosphorylation of IκB, which triggers ubiquitylation by the Ub ligase β-TRCP, followed by proteasomal IκB degradation. When NF-κB is released, it translocates to the nucleus and activates transcription. IκB, inhibitor-κB; IKK, IκB kinase; IL-1R, interleukin-1 receptor; NEMO, NF-κB essential modulator; NF-κB, nuclear factor-κB; RIP, receptor-interacting protein; TAB, TAK1-binding protein; TAK1, TGF-β-activated kinase 1; TNFR, tumor necrosis factor receptor; TRAF, TNFR-associated factor; β-TRCP, transducin-repeat-containing protein. (B) Deubiquitylation of TRAF2, TRAF6 and NEMO by the DUB CYLD leads to inhibition of NF-κB activation. Moreover, deubiquitylation of RIP by A20 is followed by A20-mediated Lys48-linked polyubiquitylation of RIP. This modification targets RIP for proteasomal degradation. CYLD, cylindromatosis. (C) During DNA damage, monoubiquitylation and Lys63-linked polyubiquitylation regulates switching between translesion and high-fidelity polymerases, leading to error-prone or error-free DNA repair, respectively. Sumolyation of PCNA is involved in DNA synthesis. Monoubiquitylation of FANCD2 is associated with DNA repair.
