Figure 5.
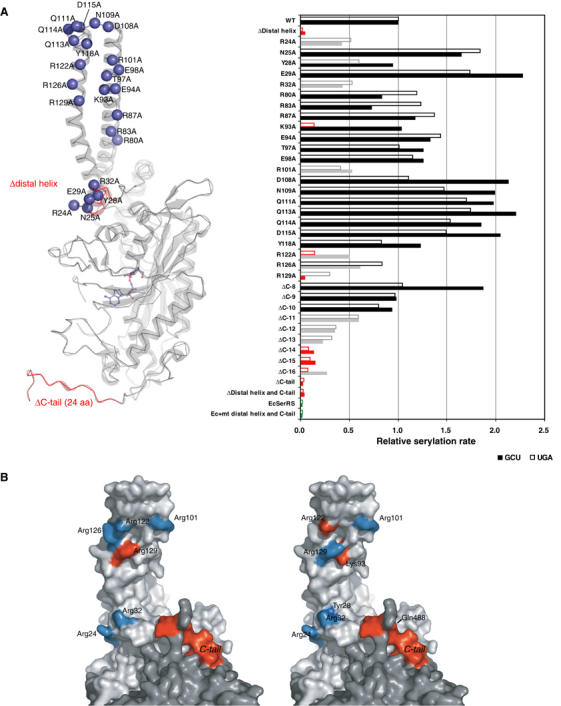
Mutagenesis studies of SerRS variants. (A) In all, 12 deletion and 23 alanine-substituted mutants of mt SerRS illustrated in the left panel, and a single mutant of E. coli SerRS with the mt N-terminal distal helix and C-tail inserted, were assayed by in vitro aminoacylation (shown in the right panel) with two native mt serine isoacceptors: tRNAsSerUGA (empty bar) and tRNAsSerGCU (filled bar). The results indicate the initial rate of serylation relative to the WT mt enzyme. Mutations retaining the serylation ability comparable to the WT are colored in black, whereas mutations that lower the serylation rate to <60% of the WT are shown in gray, and mutants that lose the serylation ability (<20%) are in red. (B) Residues involved in recognition of mt tRNASerGCU (left panel) and tRNASerUGA (right panel) are mapped onto the surface of the dimeric structure (light and dark gray for each monomer). The effective sites are colored in cyan, while the critical residues are depicted in red.
