Figure 2.
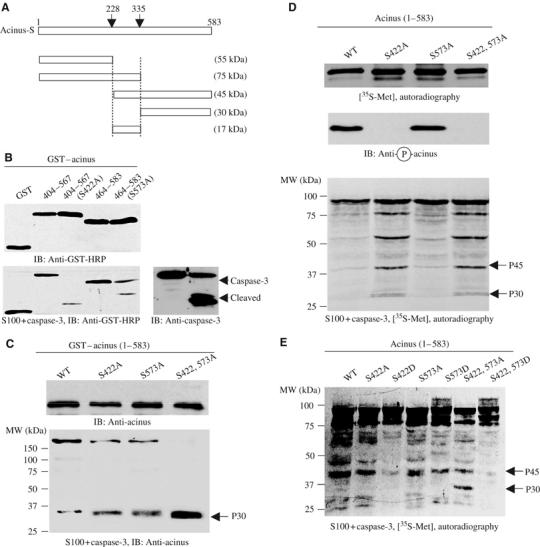
Akt phosphorylation prevents in vitro acinus proteolytic cleavage. (A) Diagram of acinus-S with putative caspase-3 cleavage sites. Residues 228–335 correspond to p17 active form in acinus-L (aa 987–1093). Caspase cleavage sites and the corresponding fragments with molecular weights were labeled. (B) Akt-phosphorylated fragments resist against apoptotic cleavage. Wild-type phosphorylated proteins resisted against apoptotic degradation, but S422A and S573A mutants were robustly cleaved in apoptotic solution (lower left panel). Equal amounts of GST proteins were employed (upper left panel). Caspase-3 was activated in the cell-free apoptotic solution (right panel). (C) Apoptotic cleavage assay with bacterial expressed full-length GST–acinus-S. Purified GST–acinus proteins were analyzed as described above. Immunoblotting was conducted with anti-acinus antibody after in vitro apoptotic degradation assay. Full-length wild type resisted against caspase cleavage, while S422A and S573A mutants were substantially degraded. Interestingly, S422, 573A mutant was almost completely cleaved. A p30 form of acinus was detected in all samples with highest amount in S422, 573A mutant (lower panel). Equal amount of GST proteins was employed (upper panel). (D) Apoptotic analysis with in vitro transcripted and translated acinus-S. Full-length acinus-S wild type and mutants were labeled with 35S-methionine in rabbit reticulocyte, and incubated with active Akt, then the reaction mixture was assayed in cell-free apoptotic solution. Prominent degradation was observed in both S422A and S422A, 573A mutants, but not in wild-type or S573A sample (bottom panel). Equal amount of 35S-labeled proteins was employed (top panel). S422 was robustly phosphorylated in both wild-type and S573A acinus (middle panel). (E) Apoptotic analysis with in vitro transcripted and translated acinus-S in the absence of Akt. Both S422D and S422, 573D mutants, but not wild-type or S573D sample, resisted against apoptotic degradation.
