Figure 1.
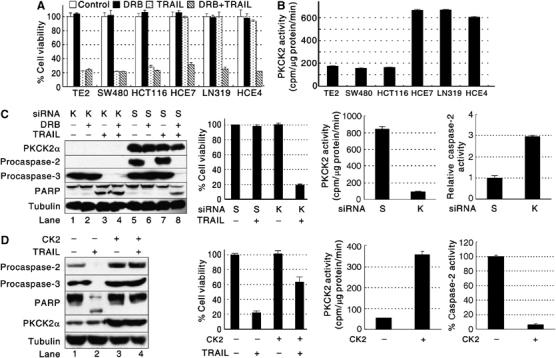
PKCK2 determines TRAIL sensitivity. (A) TRAIL cytotoxicity toward cancer cells. Cell viability was evaluated by the MTT assay using cancer cells incubated with or without DRB for 24 h and then subsequently treated with TRAIL for 2 h. The data are expressed as mean±s.d. for triplicate, and similar results were obtained from two independent experiments. (B) Endogenous PKCK2 activity in cancer cell lines. (C) Silencing of PKCK2α sensitizes cells to TRAIL. TRAIL-resistant HCE4 cells were transfected with scrambled siRNA (S) or PKCK2α SMART Pool® siRNAs (K) for 48 h and subsequently treated with DRB and/or TRAIL. Western blotting and cell viability assay were performed. PKCK2 activity and caspase-2 activity assays were performed using the siRNA-transfected cells. Relative caspase-2 activity, compared to the scrambled siRNA-transfected HCE4 cells, was calculated. (D) Acquisition of TRAIL resistance by exogenous PKCK2α expression. TRAIL-sensitive TE2 cells were transfected with an empty vector (CK2−) or with a PKCK2α expression vector (CK2+) for 24 h and subsequently incubated with TRAIL for 2 h. Western blotting and cell viability assay were performed. PKCK2 activity and caspase-2 activity assays were performed using TE2 cells transfected with an empty vector (−) or with the PKCK2α expression vector (+) for 24 h.
