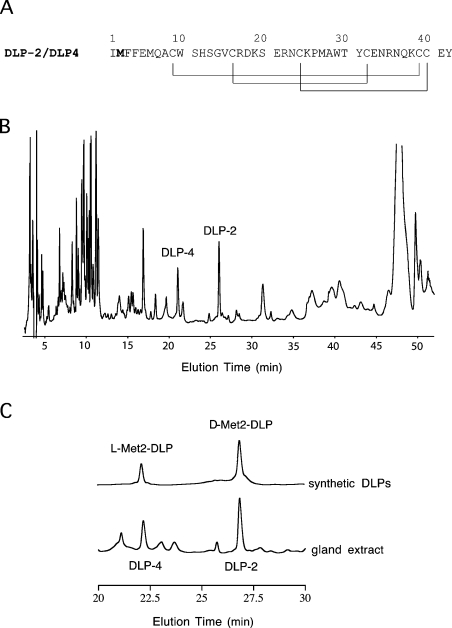
Figure 1. Primary structure and RP-HPLC of DLP-2 and DLP-4.
(A) Primary structure of DLP-2 and DLP-4. The methionine residue shown in bold is found to be in the L-form in DLP-4 and in the D-form in DLP-2. The disulphide-bonding pattern of DLP-2 as determined previously by NMR [21] is shown by lines below the sequences. It was found in the present study to be identical with that in DLP-4 based on chemical shift value comparison. (B) RP-HPLC of platypus venom gland extract. Homogenized gland (50 μl) was loaded on to a Synergi 4μ Hydro RP (250 mm×4.6 mm; Phenomenex) column in water containing 0.1% (v/v) trifluoroacetic acid. The components were eluted with a gradient of 20–45% acetonitrile containing 0.1% (v/v) trifluoroacetic acid at 1.0 ml·min−1, for 40 min at room temperature (21 °C). The absorbance was recorded at 215 nm. DLP-4 and DLP-2 eluted at ∼22 and ∼27 min respectively. (C) Sections of RP-HPLC of the venom-gland extract and solutions of synthetic DLPs. Both samples were loaded individually on to a Synergi 4μ Hydro RP (250 mm×4.6 mm; Phenomenex) column in water containing 0.1% (v/v) trifluoroacetic acid and eluted with a gradient as in (B).