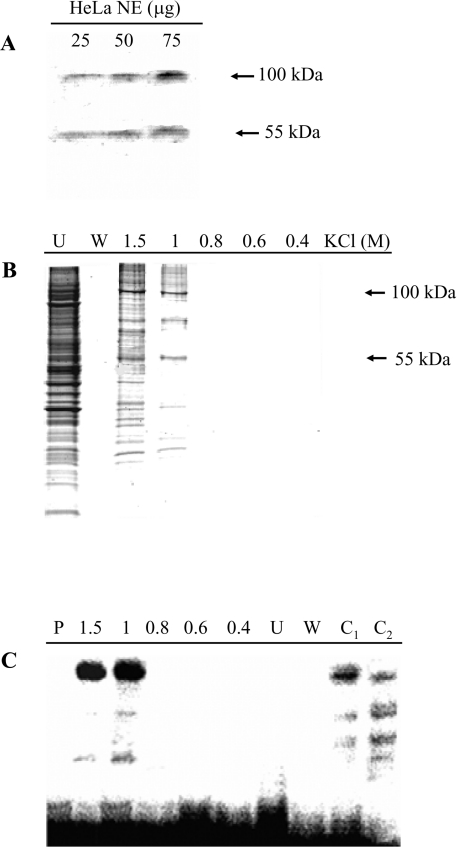
Figure 7. Identification and purification of the silencer-binding proteins.
(A) Southwestern-blot analysis. Increasing amounts of HeLa cell nuclear extracts were separated by SDS/PAGE and blotted on to a PVDF membrane, which was incubated with a 5′-end labelled DNA probe corresponding to nt −943/−919 of the PiC gene promoter (i.e. the silencer region). Specific signals are indicated by arrows. (B) Affinity purification of the silencer-binding proteins. A concatamer of the DNA sequence corresponding to nt −943/−919 of the PiC gene promoter (i.e. the silencer region) was ligated to streptavidin magnetic particles. These particles were incubated with HeLa cell nuclear extracts. The supernatant was removed with a magnetic separator and the bound proteins were separated with four washing steps and then with a buffer containing the indicated KCl concentrations. The protein fractions (30 μl) were analysed by SDS/PAGE and stained with Coomassie Blue. Lane U, supernatant; lane W, last washing step; lanes 1.5, 1, 0.8, 0.6 and 0.4, fractions eluted with 1.5, 1, 0.8, 0.6 and 0.4 M KCl. (C) Binding of the 5′-end labelled PiC gene silencer corresponding to nt −943/−919 of the PiC gene promoter to the protein fractions (30 μl) shown in (B). Lane P, labelled DNA probe only; lane C1, binding of the labelled DNA probe to 5 μg of protein of HeLa nuclear extracts; and lane C2, as in lane C1 in the presence of a 100-fold molar excess of unlabelled probe.