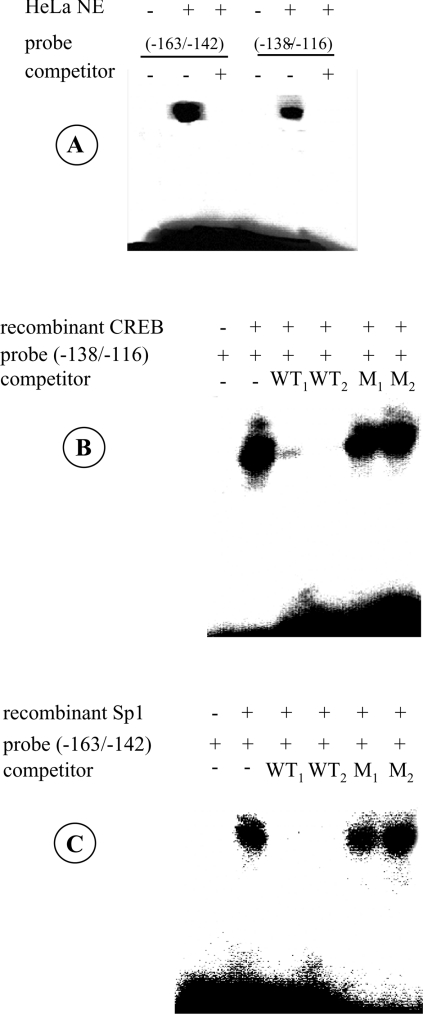
Figure 8. Specificity of protein binding to the PiC activator elements.
(A) Binding of the potential Sp1 and CREB sites within the PiC gene promoter to HeLa cell nuclear extracts. The 5′-end labelled DNA probe corresponding to nt −163/−142 or to nt −138/−116 of the PiC gene promoter was incubated with 5 μg of protein of HeLa cell nuclear extracts in the presence or absence of a 100-fold molar excess of unlabelled probe (competitor). (B) Binding of recombinant CREB to the DNA sequence from nt −138 to −116 of the PiC gene promoter. The DNA probe (−138/−116) labelled at the 5′-end was incubated with 1 μg of recombinant CREB alone and in the presence of 100- or 200-fold molar excess of the unlabelled probe (WT1 and WT2 respectively) or mutated probe (M1 and M2 respectively). The sequence of the mutated probe was GGAGAACGCGATGCATCTACGGG. (C) Binding of recombinant Sp1 to the DNA sequence from nt −163 to −142 of the PiC gene promoter. The 5′-end labelled DNA probe (−163/−142) was incubated with 2 μg of recombinant Sp1 alone and in the presence of 100- or 200-fold molar excess of the unlabelled probe (WT1 and WT2 respectively) or mutated probe (M1 and M2 respectively). The sequence of the mutated probe was GGCATTGGCTTGAATAAGGTTG.