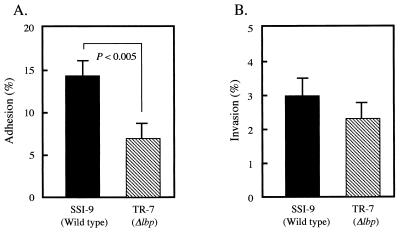
FIG. 4.
Effects of Lbp on bacterial adhesion to and invasion of HEp-2 cells. Bacteria were suspended in Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium (DMEM) containing 10% fetal bovine serum and then used to infect HEp-2 monolayers. HEp-2 cells were grown in a 24-well plate at a density of 5 × 104 per well. Approximately 107 bacteria were added to each well (multiplicity of infection, 1:200), and the plate was incubated for 3 h at 37°C. To determine bacterial adhesion, cells were washed with DMEM, lysed with 1 ml of sterile distilled water, and then plated to determine the number that were adhered to or invaded by S. pyogenes. (A) The percentage of adhesion or invasion was calculated as follows: (no. of CFU adhered to or invaded/total no. of CFU in inoculum) × 100. (B) Prior to bacterial invasion, cells were washed and incubated for 1 h in DMEM containing gentamicin (100 μg/ml) and penicillin (10 U/ml). Cells were washed, lysed, and plated for counting of those invaded by S. pyogenes. The percentage of invasion was calculated as follows: (no. of CFU invaded/total no. of CFU in inoculum) × 100. The results shown are the means ± the standard errors of the means of six wells (three experiments were performed in triplicate). Statistical analysis was performed with a nonparametric Mann-Whitney U test. All conclusions were based on a significance level of P < 0.005.