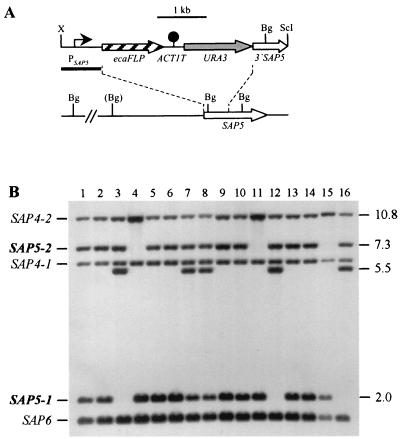
FIG. 2.
Integration of the PSAP5-ecaFLP fusion into one of the SAP5 alleles of strains CFI2 (cph1/cph1), CFI3 (efg1/efg1), and CFI4 (cph1/cph1 efg1/efg1). (A) Integration scheme. The coding regions of the SAP5 and ecaFLP genes are represented by the open and cross-hatched arrows, respectively. The SAP5 promoter (PSAP5) is indicated by the solid arrow, the ACT1 transcription termination sequence (ACT1T) is indicated by the solid circle, and the URA3 selection marker is indicated by the grey arrow. The probe used for verification of correct integration by Southern hybridization is represented by the black bar, and the diagnostic BglII sites are shown. The BglII site in parentheses is not present in the SAP5-2 allele of strain CAI4 and its derivatives. Bg, BglII; ScI, SacI; X, XbaI. (B) Southern hybridization of BglII-digested genomic DNA of parent strains and their transformants carrying the ecaFLP reporter gene with the SAP5 promoter fragment as the probe. The positions of the wild-type SAP5 alleles (boldface) and the cross-hybridizing SAP4 and SAP6 fragments are indicated on the left. The molecular sizes (in kilobases) of the wild-type SAP5 fragments and the fragments corresponding to the reporter gene fusions are indicated on the right. Lane 1, CAI4; lane 2, CFI1; lane 3, S5FI2A; lane 4, S5FI2B; lane 5, JKC18; lane 6, CFI2; lane 7, C2S5F1A; lane 8, C2S5F1B; lane 9, HLC67; lane 10, CFI3; lane 11, C3S5F1A; lane 12, C3S5F1B; lane 13, HLC69; lane 14, CFI4; lane 15, C4S5F1A; lane 16, C4S5F1B.