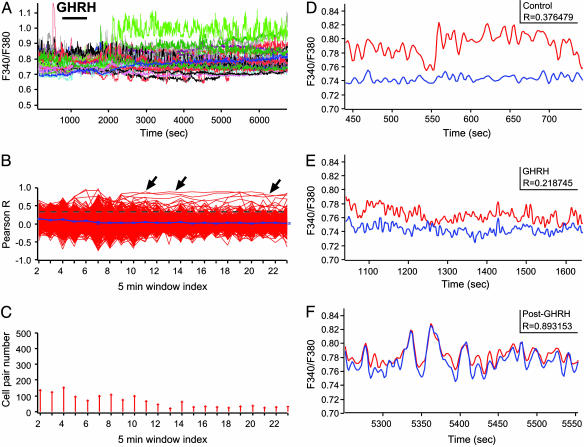
Fig. 5.
GHRH triggers sustained changes in GH cell connectivity in the median zone. (A-D) GHRH (10 nM) was applied during a 15-min time period (horizontal bar). (A) GHRH triggered a prolonged change in calcium spiking activity. (B)Cross-correlation (Pearson R) between cell pairs. Arrows indicate cell pairs with high R values after GHRH application (P < 0.001). (C) Numbers of cell pairs with significant cell connectivity (P < 0.001). Paradoxically, GHRH also caused a delayed decrease in the numbers of connected cell pairs (P < 0.05). (D-F) Changes in both calcium spike firing and cell connectivity (Pearson R) in a pair of neighboring GH cells before (D), during (E), and after (F) GHRH application. The cell pair corresponded to a trace marked by an arrow in B.