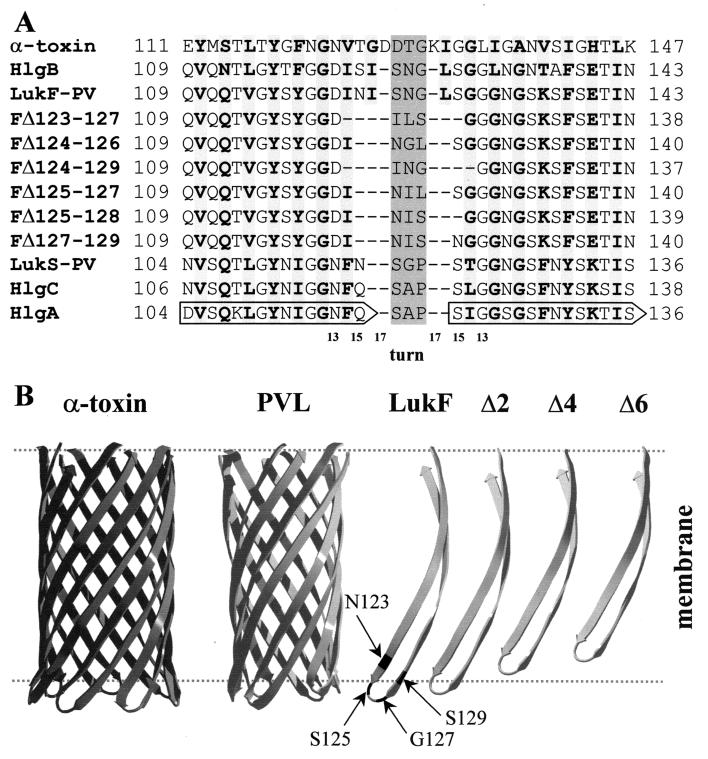
FIG. 5.
Model of the structural organization of the β-hairpins of the S and F proteins of the leucotoxin pair compared to alpha-toxin. (A) The hairpin region forming the stem of alpha-toxin is aligned to corresponding regions of the wt bicomponent toxins (18) and the deletion mutants. Based on this alignment, the turn region of each component, either wt or mutated, was assigned as a central shaded triplet of residues. The length of the strands forming the stem in the wt toxins varies between 15 and 17 residues, whereas it is from 13 to 15 aa in the deletion mutants, as indicated by the scale below the sequences. Strand residues facing the side of the membrane are in bold over lightly shaded background. Numbering is according to the leucotoxin components (GenBank-EMBL databank accession numbers X72700 for LukS-PV and LukF-PV; X81586 for HlgA, HlgC, and HlgB). (B) The structure of the β-barrel stem of alpha-toxin (21) is compared to a model of that of leucotoxins generated with the program Deep View (http://www.expasy.ch/spdbv/) (11) and adapted from reference 19. Despite strands of the latter being one or two residues shorter, the β-barrel has approximately the same length as that of alpha-toxin because of a smaller angle with respect to the pore axis. An isolated β-hairpin of LukF-PV (or HlgB) is shown to the right. Positions 123, 125, 127, and 129 are highlighted. Next to it are β-hairpins shorter by two (corresponding to the length of the S-components LukS-PV, HlgA, or HlgC), four (ΔS125-L128), or six residues (ΔI124-S129). Other deletion mutants are intermediate between the strands Δ2 and Δ6, e.g., LukF-PV ΔN123-G127. The approximate position of the lipid bilayer is indicated by dashed lines. Hairpins shorter than Δ4 are not long enough to span the membrane.