Abstract
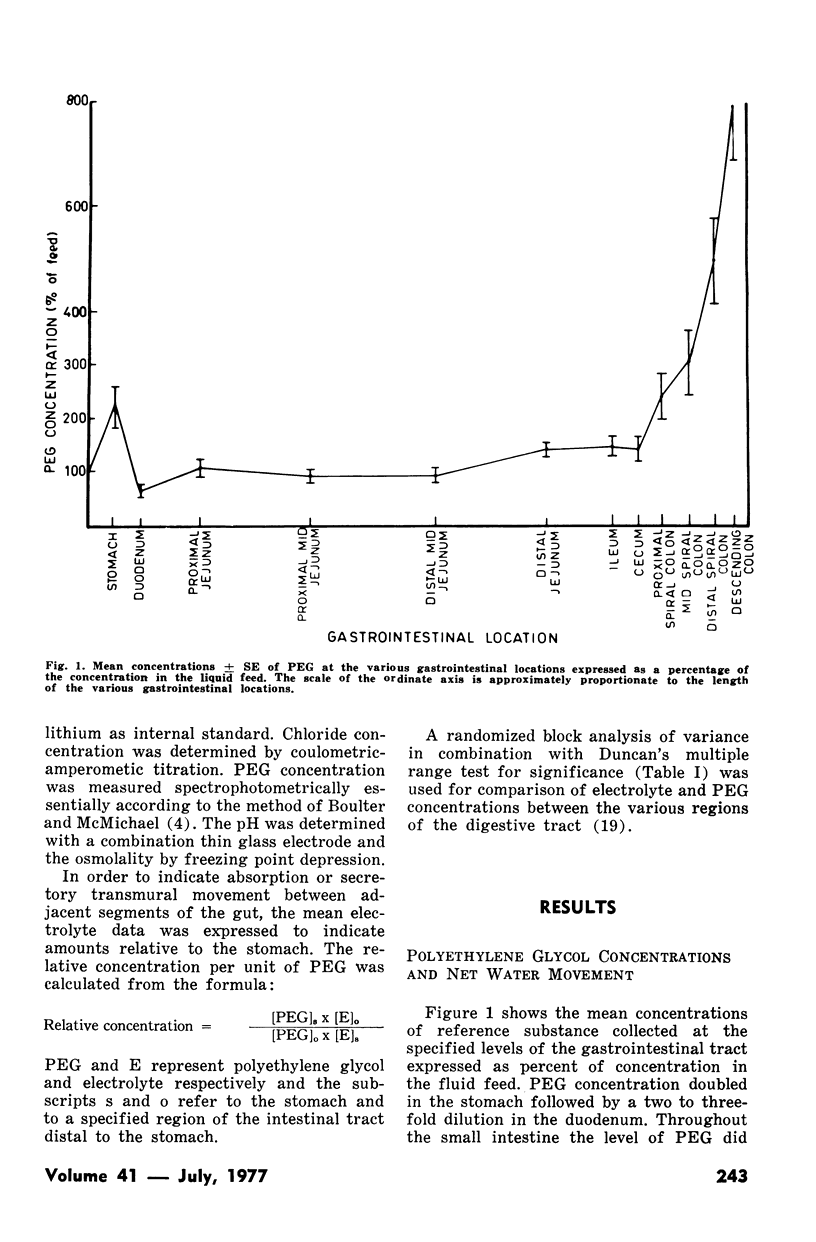
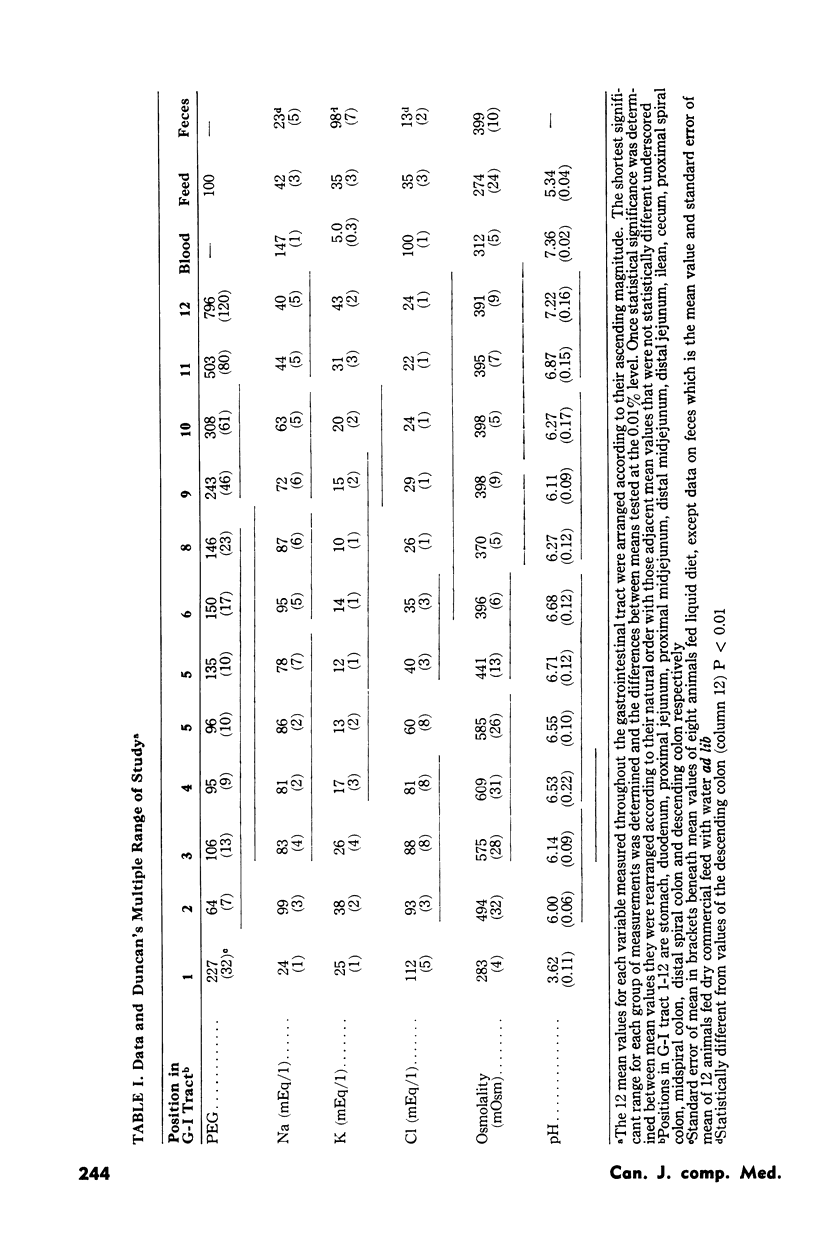
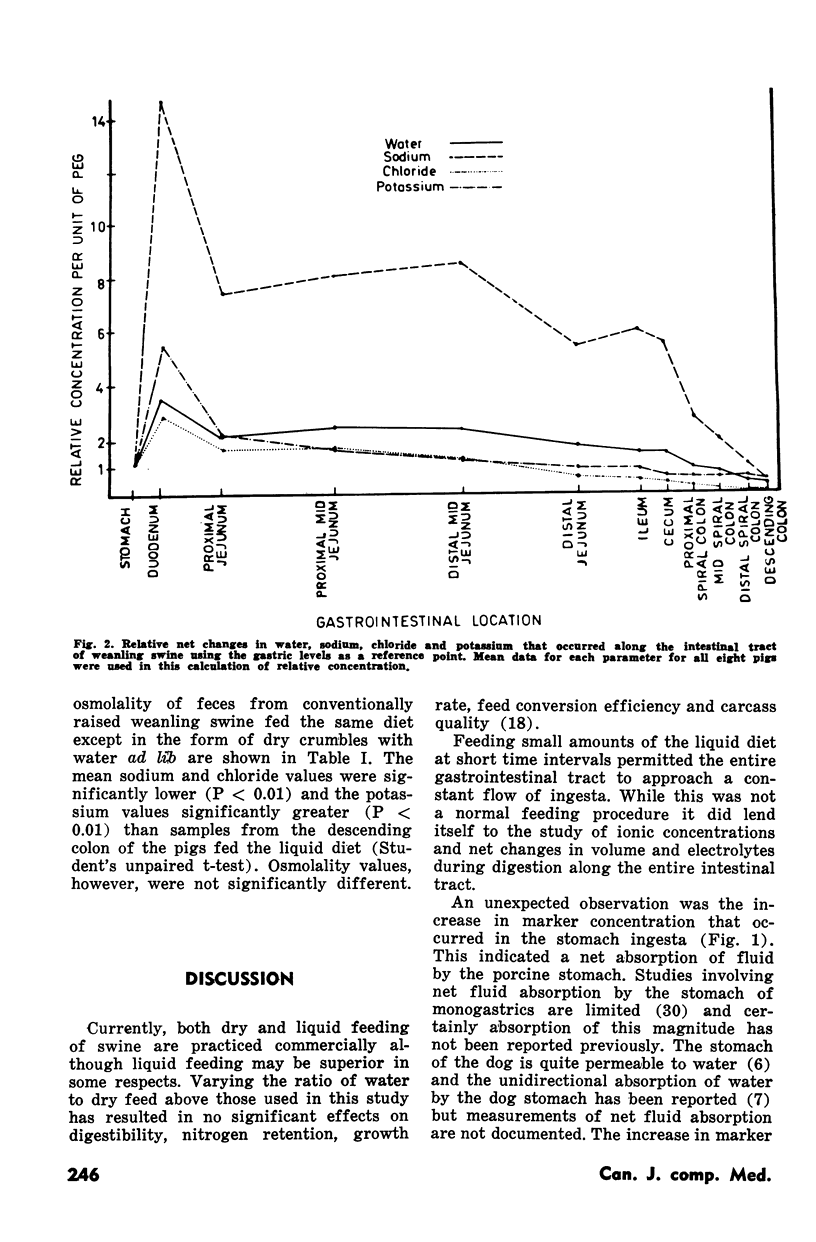
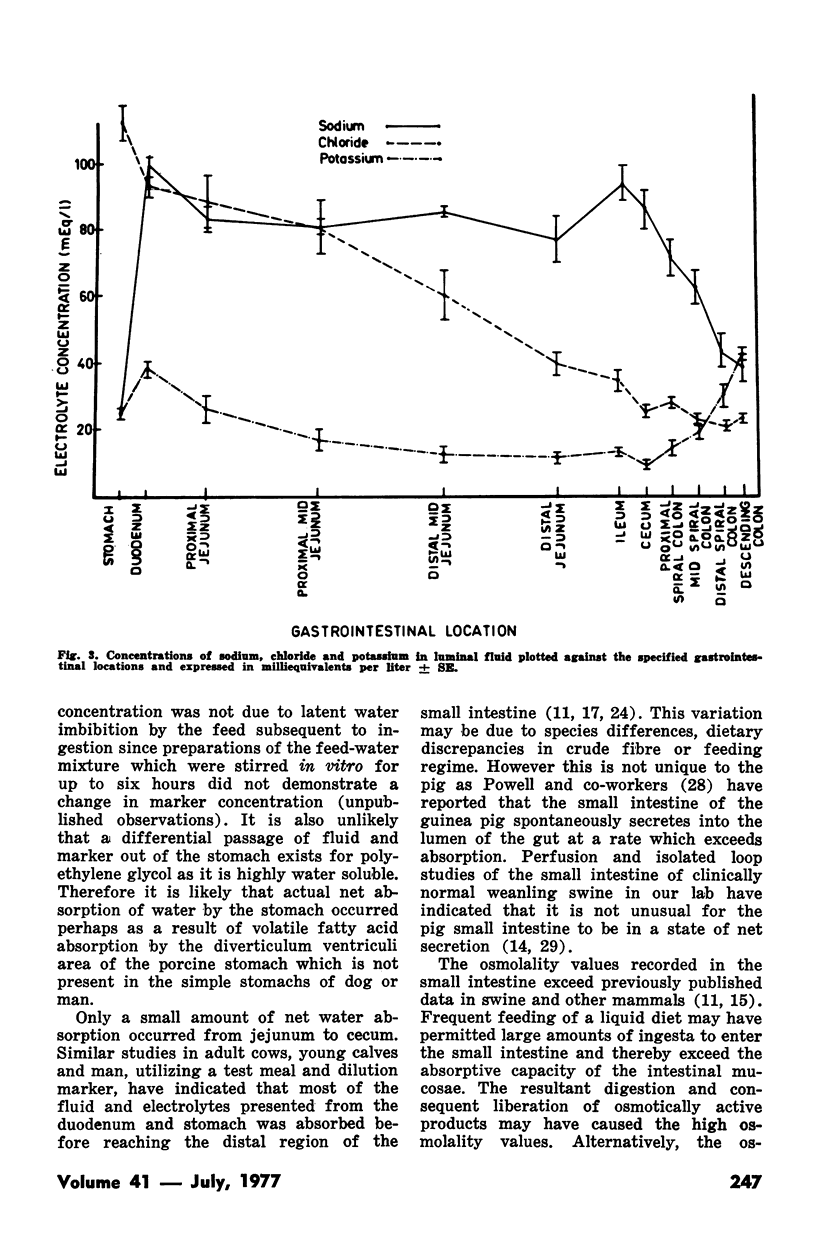
Electrolyte concentrations, osmolality and pH were determined in conventionally raised weanling swine fed a liquid diet. Incorporation of a dilution marker into the diet in combination with frequent feeding enabled estimations as to the sites of relative fluid and electrolyte absorption and secretion along the gastrointestinal tract. Unlike many other species the weanling pig depends largely on its large intestine for absorption of fluid and electrolytes with small changes in net fluid movement occurring along the jejunal and ileal segments. Additional observations included the absorption of water by the porcine stomach which increased dilution marker concentration by approximately twofold and the high osmolality values recorded in the small and large intestine. The implications of these observations are discussed with regard to pathogenesis of colibacillary diarrhea in the weanling pig.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALEXANDER F. THE CONCENTRATION OF ELECTROLYTES IN THE ALIMENTARY TRACT OF THE RABBIT, GUINEA PIG, DOG AND CAT. Res Vet Sci. 1965 Apr;6:238–244. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellamy J. E., Latshaw W. K., Nielsen N. O. The vascular architecture of the porcine small intestine. Can J Comp Med. 1973 Jan;37(1):56–62. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulter J. M., McMichael H. B. Modification of polyethylene glycol estimation suitable for use with small mammals. Gut. 1970 Mar;11(3):268–270. doi: 10.1136/gut.11.3.268. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CODE C. F., HIGGINS J. A., MOLL J. C., ORVIS A. L., SCHOLER J. F. The influence of acid on the gastric absorption of water, sodium and potassium. J Physiol. 1963 Apr;166:110–119. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007093. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clemens E. T., Stevens C. E., Southworth M. Sites of organic acid production and pattern of digesta movement in the gastrointestinal tract of swine. J Nutr. 1975 Jun;105(6):759–768. doi: 10.1093/jn/105.6.759. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cope O., Blatt H., Ball M. R. GASTRIC SECRETION. III. THE ABSORPTION OF HEAVY WATER FROM POUCHES OF THE BODY AND ANTRUM OF THE STOMACH OF THE DOG. J Clin Invest. 1943 Jan;22(1):111–115. doi: 10.1172/JCI101361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duthie H. L. Methods for studies of intestinal absorption in man. Br Med Bull. 1967 Sep;23(3):213–216. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a070558. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fordtran J. S., Locklear T. W. Ionic constituents and osmolality of gastric and small-intestinal fluids after eating. Am J Dig Dis. 1966 Jul;11(7):503–521. doi: 10.1007/BF02233563. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giller J., Phillips S. F. Electrolyte absorption and secretion in the human colon. Am J Dig Dis. 1972 Nov;17(11):1003–1011. doi: 10.1007/BF02239140. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harpur R. P., Popkin J. S. Osmolality of blood and intestinal contents in the pig, guinea pig, and Ascaris lumbricoides. Can J Biochem. 1965 Jul;43(7):1157–1169. doi: 10.1139/o65-128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendrix T. R., Bayless T. M. Digestion: intestinal secretion. Annu Rev Physiol. 1970;32:139–164. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.32.030170.001035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence T. L. A review of some effects on health and performance of variations in the physical form of the diet of the growing pig. II. Fibrous constituents and water level. Vet Rec. 1972 Jul 22;91(4):84–88. doi: 10.1136/vr.91.4.84. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mylrea P. J. Digestion of milk in young calves. I. Flow and acidity of the contents of the small intestine. Res Vet Sci. 1966 Jul;7(3):333–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mylrea P. J. Digestion of milk in young calves. II. The absorption of nutrients from the small intestine. Res Vet Sci. 1966 Oct;7(4):394–406. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen N. O., Moon H. W., Roe W. E. Enteric colibacillosis in swine. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1968 Dec 15;153(12):1590–1606. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips S. F., Code C. F. Sorption of potassium in the small and the large intestine. Am J Physiol. 1966 Sep;211(3):607–613. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1966.211.3.607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips S. F., Summerskill W. H. Water and electrolyte transport during maintenance of isotonicity in human jejunum and ileum. J Lab Clin Med. 1967 Oct;70(4):686–698. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell D. W., Binder H. J., Curran P. F. Electrolyte secretion by the guinea pig ileum in vitro. Am J Physiol. 1972 Sep;223(3):531–537. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1972.223.3.531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHOLER J. F., CODE C. F. Rate of absorption of water from stomach and small bowel of human beings. Gastroenterology. 1954 Nov;27(5):565–583. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turnberg L. A., Bieberdorf F. A., Morawski S. G., Fordtran J. S. Interrelationships of chloride, bicarbonate, sodium, and hydrogen transport in the human ileum. J Clin Invest. 1970 Mar;49(3):557–567. doi: 10.1172/JCI106266. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turnberg L. A. Potassium transport in the human small bowel. Gut. 1971 Oct;12(10):811–818. doi: 10.1136/gut.12.10.811. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


