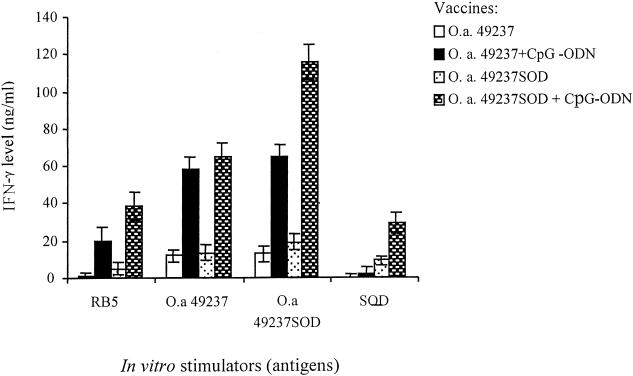
FIG. 4.
IFN-γ production by splenocytes from immunized mice upon in vitro stimulation with different antigens. BALB/c mice were inoculated i.p. with O. anthropi strain 49237 (5 × 108 CFU/mouse) or recombinant strain 49237SOD (5 × 108 CFU/mouse) with or without CpG adjuvant as described in the text. Mice were killed after 6 weeks. A total of 5 × 105 splenocytes were isolated and cultured in 96-well plates in triplicate and stimulated with either heat-inactivated B. abortus strain RB51 (106 CFU/well), O. anthropi strain 49237 (106 CFU/well), O. anthropi strain 49237SOD (106 CFU/well), or purified Cu,Zn SOD. After 5 days, supernatants were collected and tested for IFN-γ production by a sandwich ELISA. Upon stimulation with different antigens, splenocytes from mice immunized with O. anthropi strain 49237 or 49237SOD in combination with CpG-ODN produced significantly more IFN-γ than splenocytes from mice immunized with the respective strains without CpG-ODN (P < 0.05). The heat-inactivated O. anthropi strain 49237SOD stimulated significantly higher IFN-γ production by splenocytes from mice immunized with strain 49237SOD plus CpG-ODN than by splenocytes from mice immunized with strain 49237 plus CpG-ODN (P < 0.05). Stimulations with heat-inactivated RB51 or purified Cu,Zn SOD also resulted in significant differences in IFN-γ production between mice immunized with O. anthropi strain 49237SOD with and without CpG-ODN coinjection (P < 0.05).