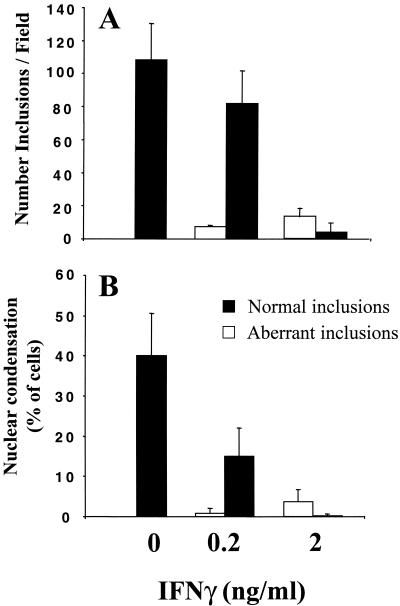
FIG. 3.
Sensitivity to the effects of IFN-γ and correlation between the developmental state of Chlamydia vacuoles and sensitivity to apoptosis. HeLa cells were infected with C. muridarum at an MOI of 0.5 for 48 h in the presence of the indicated concentrations of IFN-γ. (A) The number of cells containing normal inclusions (black bars) or inclusions with persistent chlamydiae (white bars) was determined and defined as described in Materials and Methods. For cells containing normal inclusions, P is <0.01 for 0 versus 0.2 and 0 versus 2 ng of IFN-γ per ml. (B) Host cells were identified as containing normal or persistent chlamydiae, and apoptotic cells were counted based on the condensation of Hoechst-labeled nuclei, as described in Materials and Methods. For cells containing normal inclusions and condensed nuclei, P is <0.001 for 0 versus 2 ng of IFN-γ per ml and <0.01 for 0 versus 0.2 ng of IFN-γ per ml. Each series of experiments was performed at least three times.