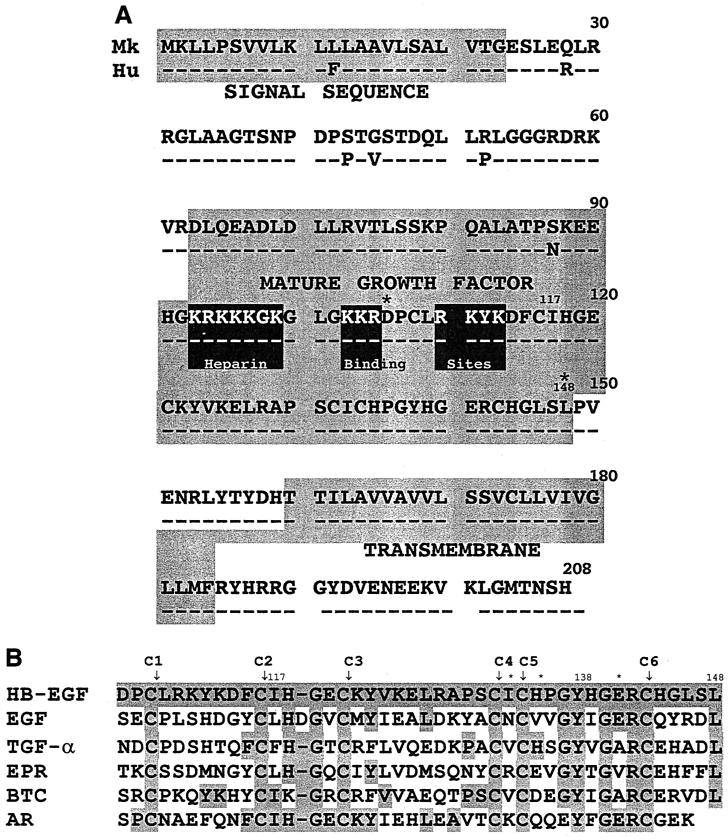
FIG. 1.
(A) Comparison of Mk (upper line) (34) and human (Hu) (lower line) (23) HB-EGF precursors. Identical amino acid residues are denoted by dashes, and differing residues are denoted by their single-letter amino acid code. The signal sequence, mature growth factor domain, and the transmembrane domain are indicated by shaded boxes and are based on the designations of Abraham et al. (1). Three stretches of basic amino acids in the HB domain (93KRKKKGK, 103KKR, and 110RKYK) are indicated by the three black boxes. Ile117 and Leu148 are indicated by the residue number. The beginning (residue 106) and the end (residue 148) of the EGF-like domain are denoted by asterisks. (B) EGF-like domains sequence comparison of Hu HB-EGF with the other members of the Hu EGF family. EPR, epiregulin. All sequences were obtained from GenBank. The numbers at the top refer to the position of the residues in the Mk HB-EGF precursor, including the signal sequence shown in panel A (34). The shaded boxes indicate residues that are identical to those in Mk HB-EGF. The characteristic six conserved cysteine residues, which form three disulfide bonds (linked C1—C3, C2—C4, and C5—C6), are marked with arrows. Critical residues (I133, H135, and E141) for DT binding are marked with asterisks. The residues noted for Hu EGF correspond to residues 4 to 47 of its mature form, the residues noted for Hu TGF-α correspond to residues 6 to 48 of its mature form, the residues noted for Hu epiregulin correspond to residues 4 to 46 of its mature form, the residues noted for Hu BTC correspond to residues 36 to 78 of its mature form, and the residues noted for Hu AR correspond to residues 44 to 84 of its mature form (41).