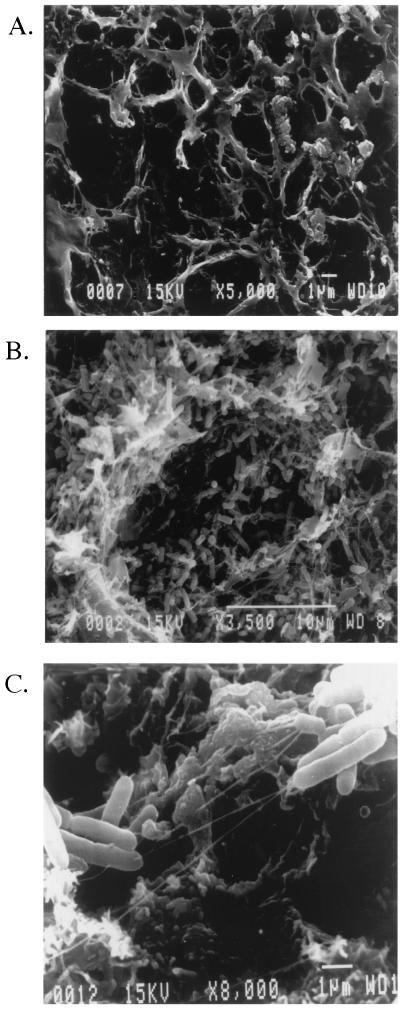
FIG. 2.
SEM micrographs of S. enterica serovar Typhimurium biofilm formation on the surfaces of human gallstones. (A) Example of the gallstone surface on which Salmonella are most commonly found. The gallstone was grown in the presence of bacteria in LB broth alone, and the results demonstrate that salmonellae do not form a biofilm or adhere to the surface unless bile is present in the medium. (B) Wild-type Salmonella cells exposed to a human gallstone for 14 days in the presence of LB broth containing 3% bile are loosely dispersed over the surface of a gallstone with apparent desiccated EPS. (C) Increased magnification of panel B, showing the web-like strands connecting bacteria both to other bacteria and to the gallstone surface.