Abstract
Three classes of events were scored from videotapes of 14 college basketball games during the 1989 National Collegiate Athletic Association tournament: reinforcers (such as points and favorable turnovers), adversities (such as missed shots, unfavorable turnovers, and fouls), and responses to adversities (favorable or unfavorable outcomes of the first possession of the ball following an adversity). Within-game and within-team analyses of these data supported three findings. First, a team's favorable response to an adversity generally increased as the rate of reinforcement increased 3 min preceding the adversity. Second, basketball coaches called time-out from play when being outscored by their opponents an average of 2.63 to 1.0. Third, calling time-outs from play appeared to be an effective intervention for reducing an opponent's rate of reinforcement. Rates of reinforcement during the 3 min immediately after a time-out were nearly equal for both teams. Results are discussed within a behavioral momentum framework.
Keywords: behavioral momentum, sports behavior analysis, resistance to change, basketball
Full text
PDF

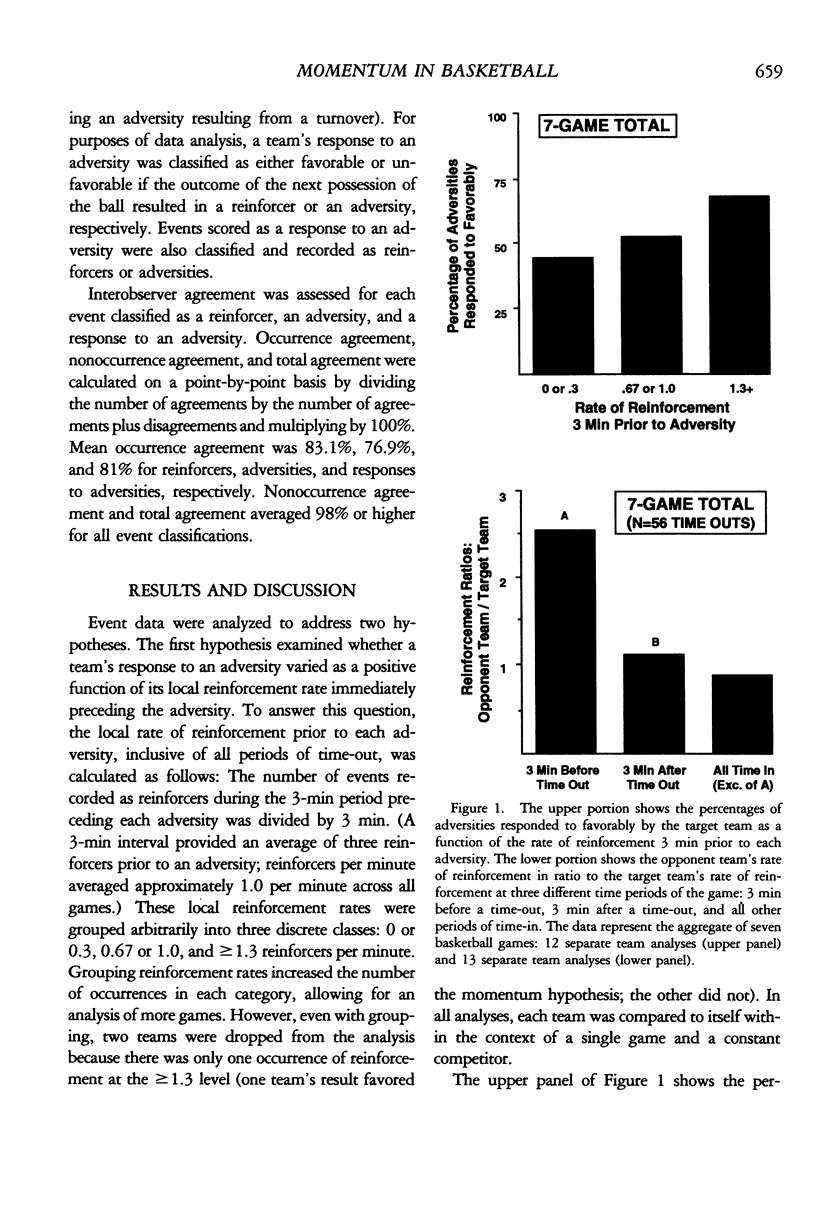
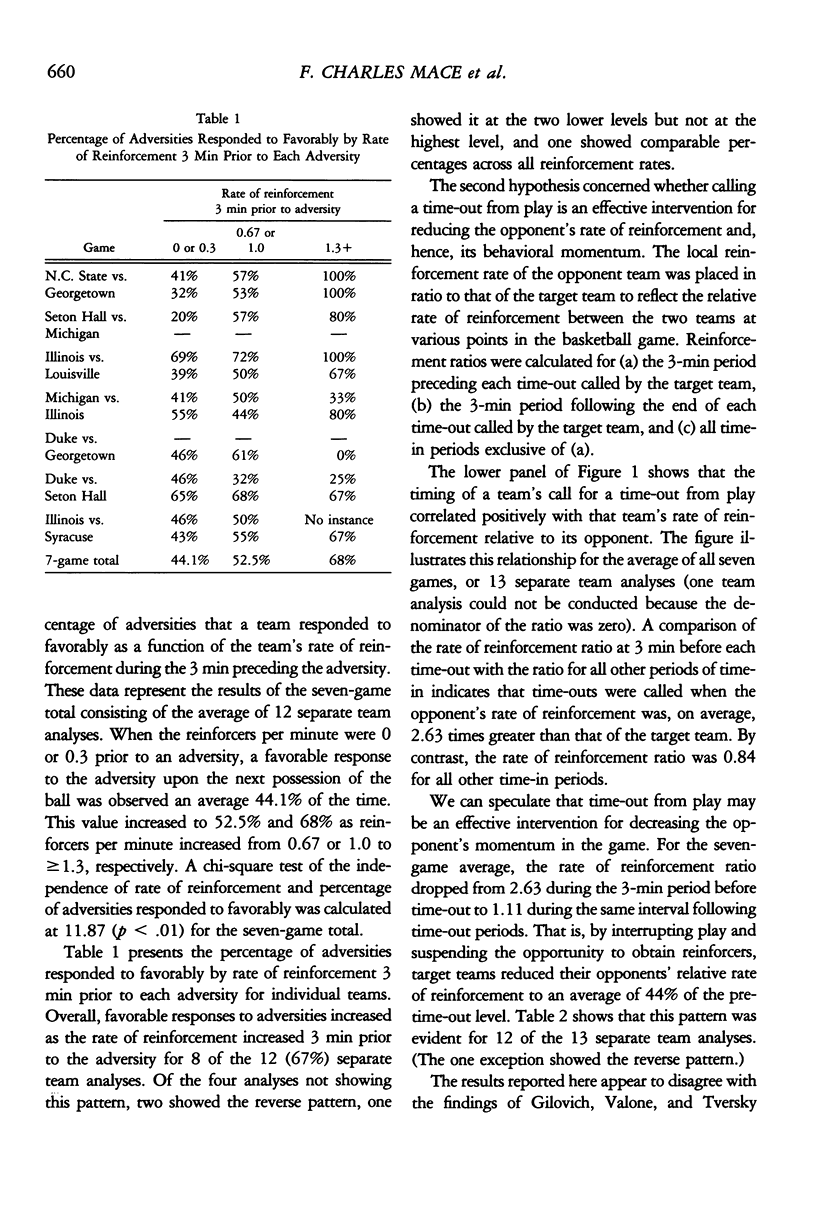


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baum W. M. Choice in free-ranging wild pigeons. Science. 1974 Jul 5;185(4145):78–79. doi: 10.1126/science.185.4145.78. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graft D. A., Lea S. E., Whitworth T. L. The matching law in and within groups of rats. J Exp Anal Behav. 1977 Jan;27(1):183–194. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1977.27-183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grott R., Neuringer A. Group behavior of rats under schedules of reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1974 Sep;22(2):311–321. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1974.22-311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mace F. C., Hock M. L., Lalli J. S., West B. J., Belfiore P., Pinter E., Brown D. K. Behavioral momentum in the treatment of noncompliance. J Appl Behav Anal. 1988 Summer;21(2):123–141. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1988.21-123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mace F. C., Lalli J. S., Shea M. C., Lalli E. P., West B. J., Roberts M., Nevin J. A. The momentum of human behavior in a natural setting. J Exp Anal Behav. 1990 Nov;54(3):163–172. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1990.54-163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan M. J., Fitch M. D., Holman J. G., Lea E. G. Pigeons learn the concept of an "A". Perception. 1976;5(1):57–66. doi: 10.1068/p050057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevin J. A., Tota M. E., Torquato R. D., Shull R. L. Alternative reinforcement increases resistance to change: Pavlovian or operant contingencies? J Exp Anal Behav. 1990 May;53(3):359–379. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1990.53-359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


