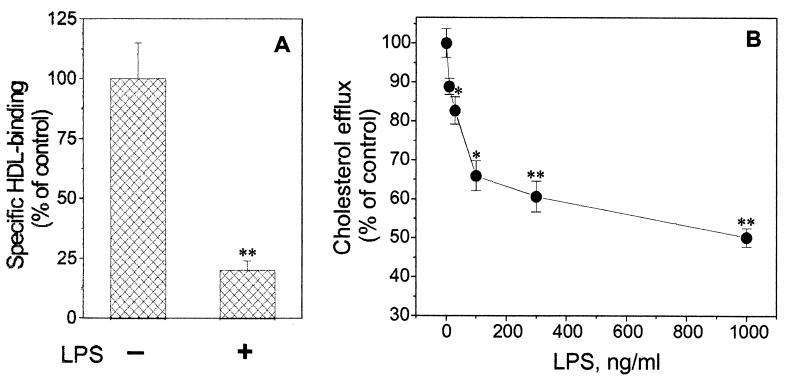
FIG. 3.
Down regulation of specific HDL binding and HDL-mediated cholesterol efflux by LPS. (A) Effect of LPS on 125I-HDL specific binding in RAW cells. The cells were incubated with 1 μg of LPS per ml for 24 h. Following three PBS washes, the specific binding of 125I-HDL (5 μg/ml) was determined at 4°C as the difference between the total and nonspecific binding (in the absence or presence of a 50-fold excess of unlabeled HDL). (B) Dose-dependent response of HDL-mediated [3H]cholesterol efflux to LPS stimulation. RAW cells preloaded with cholesterol were labeled with 1 μCi of [1,2-3H]cholesterol (50 Ci/mmol) per ml. Before the cholesterol efflux determination, the cells were pretreated with the increasing concentrations (0 to 1,000 ng/ml) of LPS for 24 h. After HDL (100 μg/ml) as the cholesterol acceptor was added, the [3H]cholesterol efflux assay was performed after an additional 24 h. Cholesterol efflux was calculated as the amount of radioactivity present in the medium divided by the total radioactivity (medium plus cell) in each well. The data shown represent one of two independent experiments that yielded similar results. ∗, P < 0.05; ∗∗, P < 0.01 (compared to untreated control samples). Error bars indicate standard deviations.