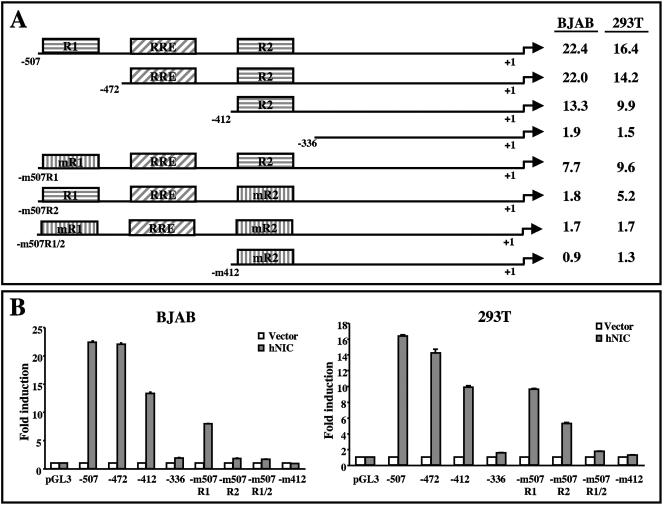
FIG. 5.
Activation of vIL-6 expression induced by hNIC. (A) Schematic diagrams of the potential RBP-Jκ binding sites within the vIL-6 promoter region. The positions of the two putative RBP-Jκ binding sequences (R1 and R2), the mutations at the RBP-Jκ binding sequences (mR1 and mR2), and the RTA-responsive elements (RRE) are shown. The numbers below the maps indicate the position relative to the translational start site (+1). The numbers to the right of the figure indicate the increase in induction in BJAB and 293T cells upon hNIC expression over the control vector expression. (B) Luciferase assay. Wild-type (pGL3) or mutant vIL-6 promoter luciferase reporter together with the pGK-β-gal construct was transfected into BJAB or 293T cells with pcDNA5 vector (Vector) or pDNA5-hNIC (hNIC). The mutant vIL-6 promoter luciferase reporters used were pvIL-6(−507), pvIL-6(−472), pvIL-6(−412), pvIL-6(-m507R1), pvIL-6(-m507R2), pvIL-6(-m507R1/2), and pvIL-6(-m412) (only the last part of the plasmid designation is shown in the figure). At 48 h posttransfection, cell lysates were used for reporter assays. Luciferase activity is presented as the average of three independent experiments.