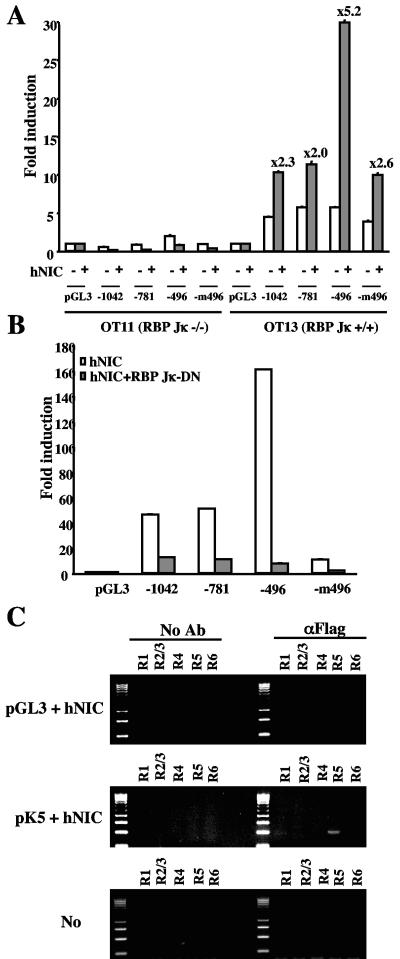
FIG. 8.
Role of RBP-Jκ in the hNIC-mediated activation of K5 promoter activity. (A) hNIC-mediated activation of K5 requires RBP-Jκ expression. RBP-Jκ−/− OT11 and RBP-Jκ+/+ OT13 MEFs were transfected with K5 promoter luciferase reporters and pGK-β-gal together with pcDNA5 vector or pDNA5-hNIC. The K5 promoter luciferase reporters used pK5(−1042), pK5(−781), pK5(−496), pK5(−232), and pK5(-m496) (only the last part of the plasmid designation is shown in the figure). At 48 h posttransfection, cell lysates were used for reporter assays. Luciferase activity is presented as the average of three independent experiments. (B) Inhibition of the hNIC-induced activation of K5 promoter activity by RBP-Jκ dominant-negative (DN) mutant. Wild-type (pGL3) or mutant K5 promoter luciferase reporter together with pGK-β-gal was transfected into 293T cells with pDNA5-hNIC alone or with pcDNA5-hNIC and pcDNA5-RBP-Jκ DN vectors. At 48 h posttransfection, cell lysates were used for reporter assays. Luciferase activity is presented as the average of three independent experiments. (C) CHIP assay. 293T cells were transfected with pGL3 and pcDNA5-hNIC or pK5(−1042) and pcDNA5-hNIC or not transfected with DNA (No). At 48 h posttransfection, cell lysates were used for immunoprecipitation with an anti-Flag antibody (αFlag) or without antibody (No Ab). Then, immune complexes were used for PCR analysis with primers to specifically amply the R1, R2/3, R4, R5, and R6 RBP-Jκ binding sequences. PCR products were separated by 3% agarose gel electrophoresis.